Key Takeaways
Complete guide to creating student mentorship programs using digital alumni discovery boards including benefits, implementation strategies, platform features, and best practices for connecting students with alumni mentors.
Understanding Student Mentorship Alumni Discovery Boards
Before diving into implementation details, understanding what makes these systems effective and how they differ from traditional alumni directories provides important context for planning your program.
What Is an Alumni Discovery Board?
An alumni discovery board is an interactive digital platform—whether screen-based touchscreen displays, web applications, or mobile apps—that allows students to explore alumni profiles, achievements, and career paths while facilitating connections for mentorship, networking, and professional guidance.
Unlike traditional printed alumni directories that simply list names and basic information, modern discovery boards transform alumni data into engaging, searchable experiences that help students identify relevant mentors based on career interests, industry, location, expertise areas, and shared backgrounds or experiences.

These platforms bridge the gap between students seeking guidance and alumni willing to provide mentorship by making connections visible, accessible, and actionable rather than leaving students to navigate complex networking processes without clear pathways.
The Evolution from Directories to Discovery Platforms
Traditional alumni directories served primarily as reference tools for alumni seeking to reconnect with classmates. Modern discovery boards represent a fundamental shift in purpose and functionality, moving from passive information storage to active matchmaking and engagement tools designed specifically to facilitate student-alumni connections.
Key differences include:
Search and Discovery Functionality
Traditional directories offered limited search capabilities—typically just name, graduation year, or basic location filters. Discovery boards provide sophisticated filtering by career field, industry, expertise areas, willingness to mentor, geographic proximity, and shared interests or backgrounds enabling students to identify highly relevant mentors quickly.
Rich Multimedia Profiles
Instead of text-only listings, modern platforms feature comprehensive profiles including professional headshots, career trajectory timelines, video introductions from alumni, achievement highlights and recognition, areas where alumni can provide guidance, and testimonials from previous mentees.
Built-In Communication Tools
Discovery boards integrate messaging systems, meeting scheduling, video conferencing, mentorship request workflows, and connection tracking rather than requiring students to find contact information and reach out through unstructured channels where many students feel uncomfortable initiating contact.
Engagement Tracking and Analytics
Modern systems capture data on which alumni profiles students view most frequently, what filters students use when searching, which mentorship matches prove most successful, student engagement patterns and preferences, and program effectiveness metrics informing continuous improvement.
The Compelling Benefits of Student-Alumni Mentorship Programs
The research supporting student-alumni mentorship is remarkably consistent across institutional types and program structures, demonstrating significant positive impacts on multiple stakeholder groups.
Benefits for Students
Enhanced Academic Performance and Persistence
Students participating in mentorship programs demonstrate 20-30% higher retention rates compared to non-participants, according to multiple studies across academic and professional settings. At Louisiana State University, 74-77% of students in mentoring programs graduated compared to 55.9% of the general STEM student population, representing a substantial improvement in degree completion.
Mentorship provides accountability, encouragement during challenging periods, study strategies and academic guidance, connections to campus resources students might not otherwise discover, and perspective from someone who successfully navigated similar challenges.
Improved Career Readiness and Job Placement
The career development benefits are particularly striking. Students in the Leeds School of Business at the University of Colorado, Boulder mentoring program were 40% more likely to have a job upon graduation than non-participants. Furthermore, 70% of participating students felt more confident about finding work, and 80% felt more equipped to discuss their skill sets with potential employers.
Career guidance from alumni provides students with industry insights not available through traditional coursework, realistic expectations about career paths, networking strategies and professional etiquette, resume and interview preparation from hiring perspectives, and often direct connections to internship and employment opportunities.
Expanded Professional Networks
Mentorship relationships create entry points into professional networks that might otherwise remain inaccessible to students without family connections or prior industry experience. Alumni mentors introduce students to industry contacts, invite mentees to professional events and conferences, provide recommendations and references, and serve as ongoing career resources extending far beyond graduation.

Increased Confidence and Engagement
Beyond tangible academic and career outcomes, mentorship significantly impacts student confidence and institutional engagement. According to program evaluations, 75% of students reported being more satisfied with their educational experience after participating in mentorship programs, and 95% said they were more likely to want to become mentors themselves in the future, creating sustainable cycles of giving back.
Benefits for Alumni Mentors
While student benefits typically drive program development, the value proposition for alumni participants is equally important for securing ongoing mentor engagement.
Professional Fulfillment and Purpose
Alumni consistently report that mentoring provides deep professional fulfillment by allowing them to give back to institutions that shaped their trajectories, see direct positive impact on students’ lives, stay connected to their alma mater in meaningful ways, and rediscover purpose through helping others navigate challenges they once faced.
According to research on mentoring, 91% of professionals with mentoring relationships report higher job satisfaction, and 79% consider mentoring crucial for career success, indicating that the benefits flow in both directions.
Skill Development and Reflection
Serving as a mentor helps alumni develop or strengthen leadership and coaching abilities, communication and listening skills, patience and empathy, and self-awareness through articulating career lessons and reflecting on their own professional journeys. Many alumni report that explaining concepts to mentees helps clarify their own thinking and improves their ability to communicate complex ideas to diverse audiences.
Expanded Professional Networks
Mentorship creates networking opportunities for alumni as well as students. Alumni mentors connect with other accomplished graduates through mentor networks and events, gain insights into emerging trends through conversations with current students, identify potential talent for hiring opportunities at their organizations, and strengthen relationships with institutional leadership and career services professionals.
Benefits for Educational Institutions
From an institutional perspective, effective student-alumni mentorship programs provide strategic advantages across multiple dimensions.
Improved Student Outcomes and Institutional Metrics
The academic persistence, graduation rates, and job placement improvements documented earlier directly enhance institutional rankings, accreditation outcomes, enrollment marketing appeals, and overall institutional reputation. When schools can demonstrate that 40% more mentored students secure employment upon graduation, that messaging powerfully differentiates institutions in competitive markets.
Strengthened Alumni Engagement and Giving
Alumni who serve as mentors demonstrate significantly higher engagement across all measures including event attendance, volunteer participation, philanthropic giving, referral of prospective students, and advocacy for the institution. Research on alumni engagement consistently shows that volunteers give more time and money than non-volunteers, and mentorship represents one of the most meaningful volunteer opportunities institutions can offer.
Enhanced Institutional Culture and Identity
Visible mentorship programs strengthen institutional culture by demonstrating commitment to student success beyond classroom instruction, creating tangible connections between current students and institutional legacy, building traditions of giving back and community support, and fostering pride among all stakeholders in the institution’s student-centered mission.
Designing Your Student Mentorship Alumni Discovery Board
Creating an effective discovery board requires careful consideration of platform options, feature priorities, user experience design, and integration with broader mentorship programming.
Platform Options: Physical Displays vs. Digital Applications
Student mentorship alumni discovery boards can take multiple forms, each offering distinct advantages depending on institutional context and goals.
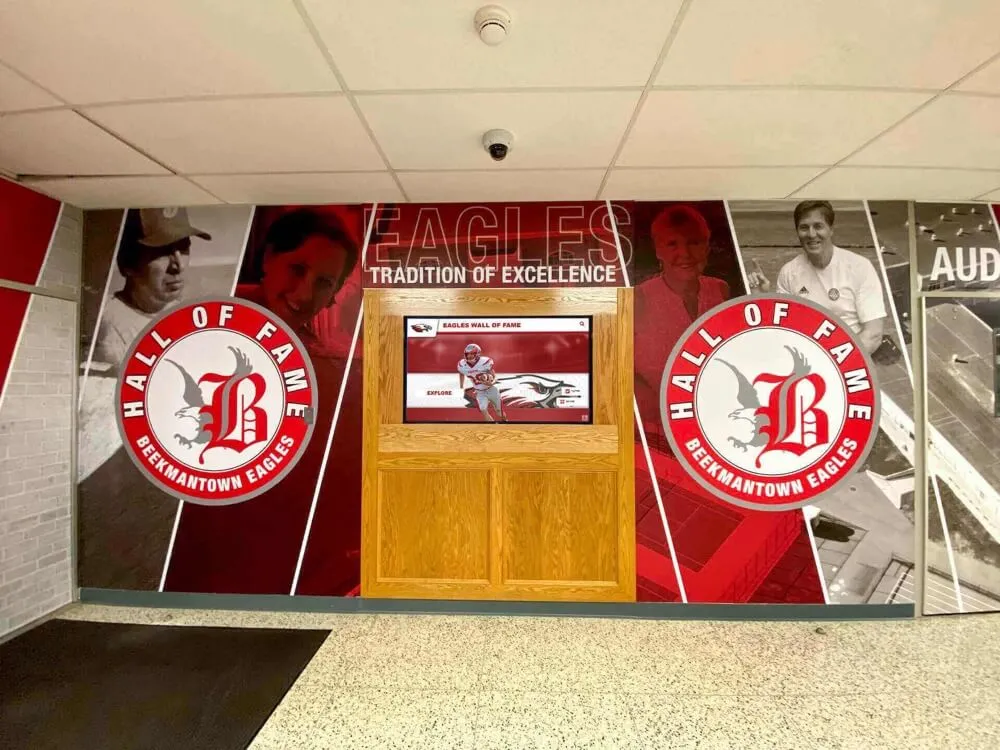
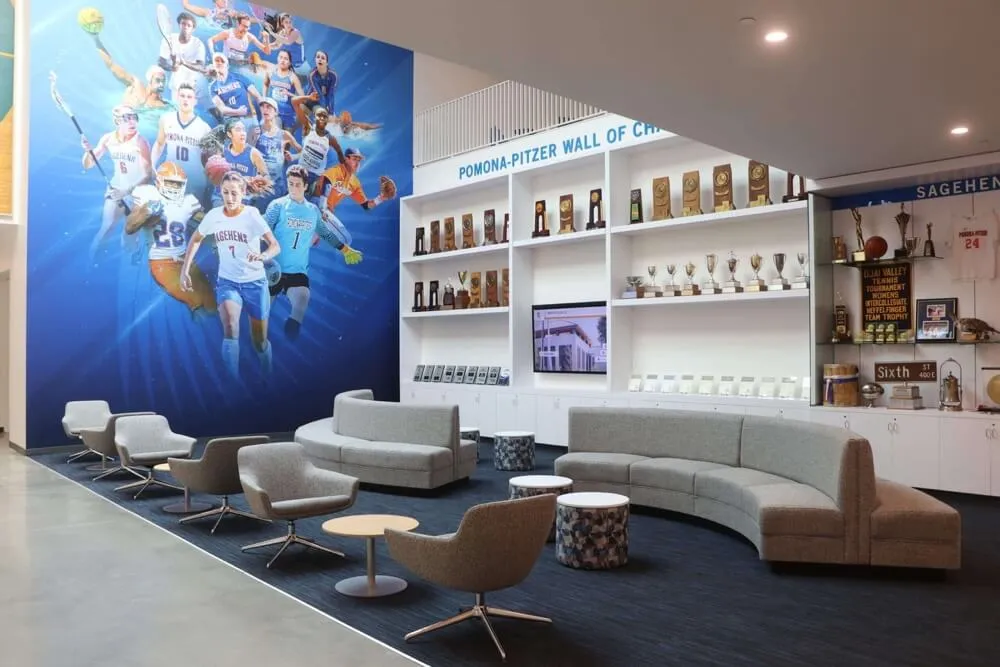
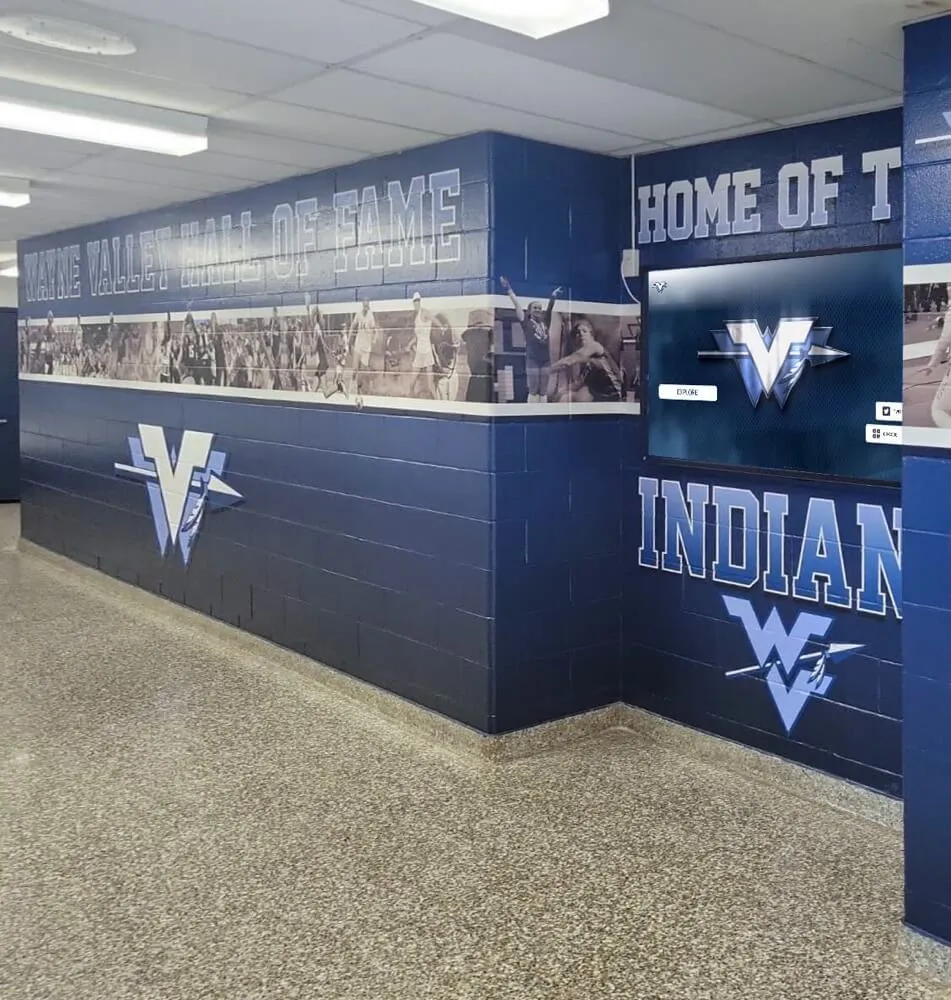
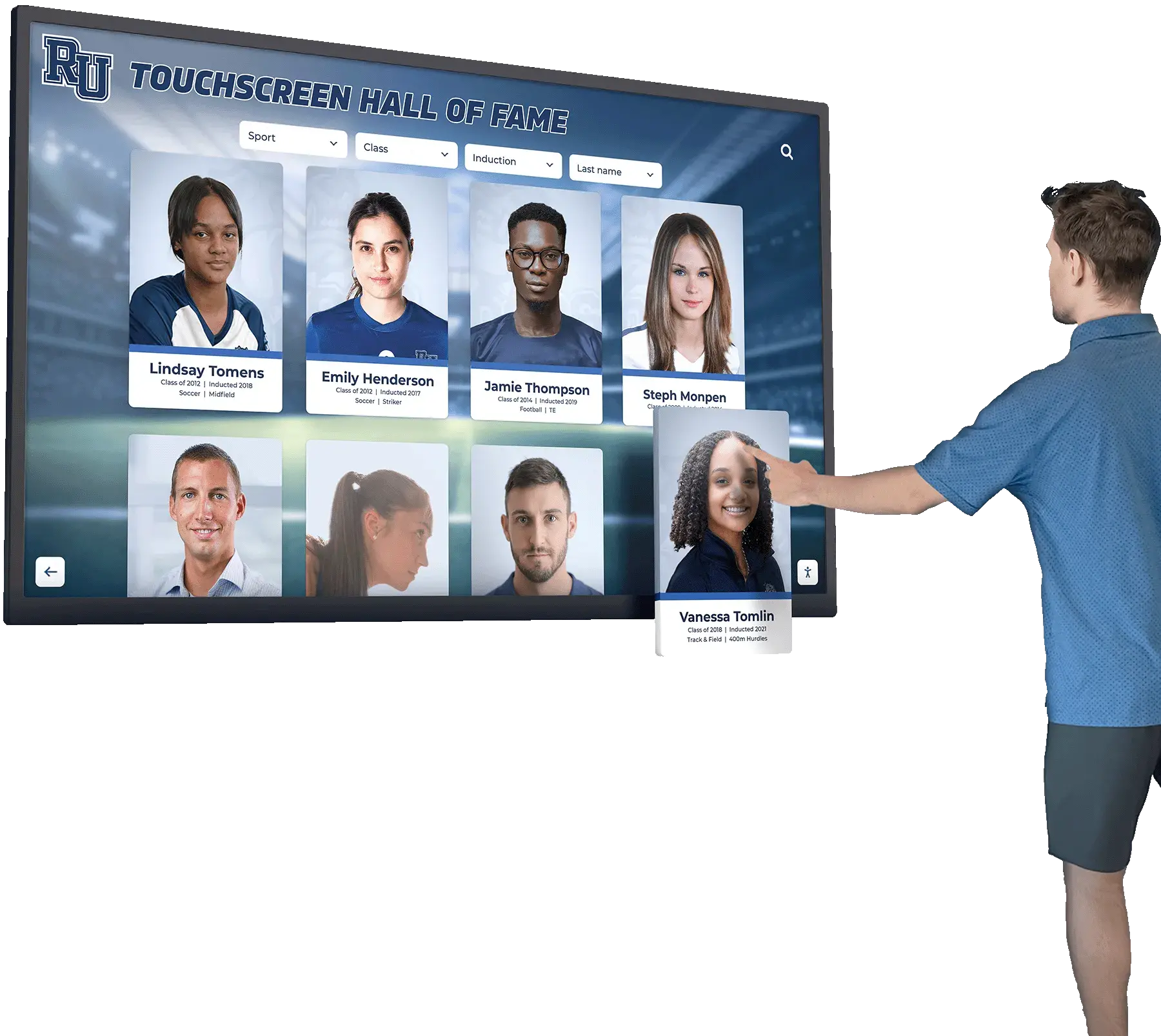
Interactive Touchscreen Displays
Physical touchscreen displays installed in strategic campus locations provide highly visible, accessible discovery experiences that integrate seamlessly into students’ daily campus navigation.
Key advantages include:
- High visibility creating awareness among students who might not actively seek mentorship
- No login barriers allowing casual exploration without accounts or passwords
- Engaging multimedia experiences with large screens showcasing compelling visual content
- Physical presence signaling institutional commitment to alumni-student connections
- Accessibility for students without personal devices or reliable internet access
- Social discovery where groups of students can explore together, often making discovery more comfortable than solitary searching
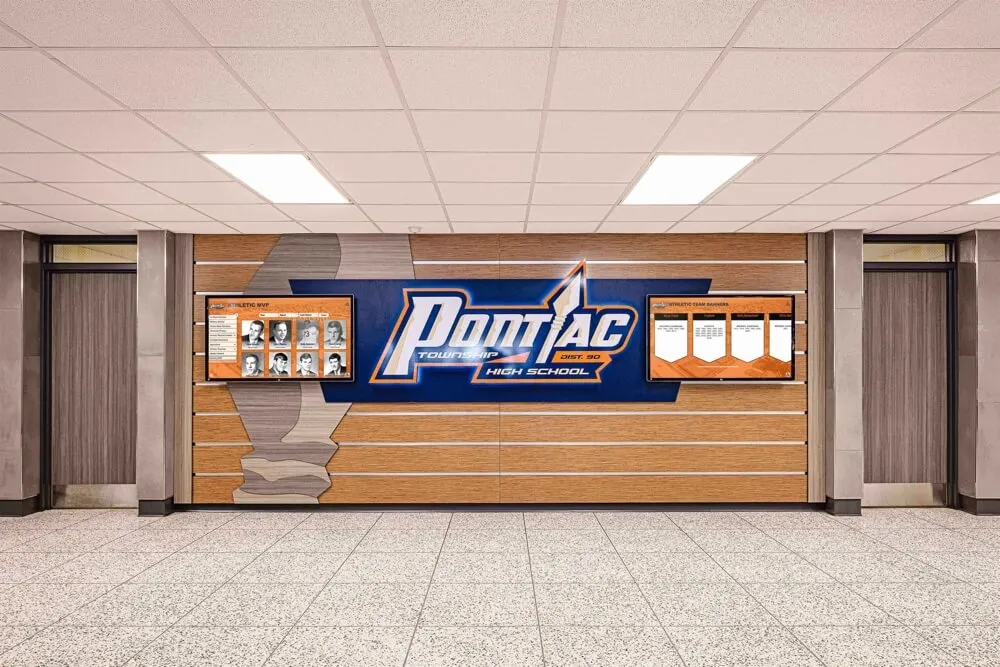
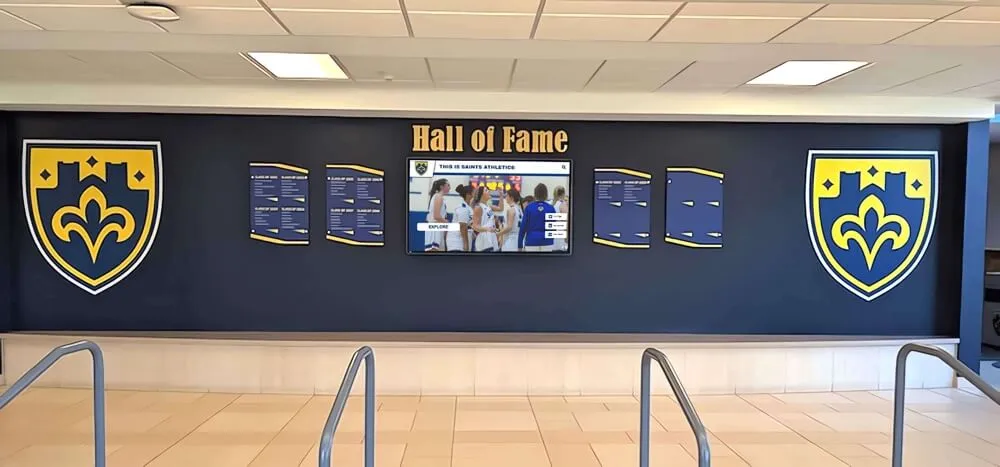
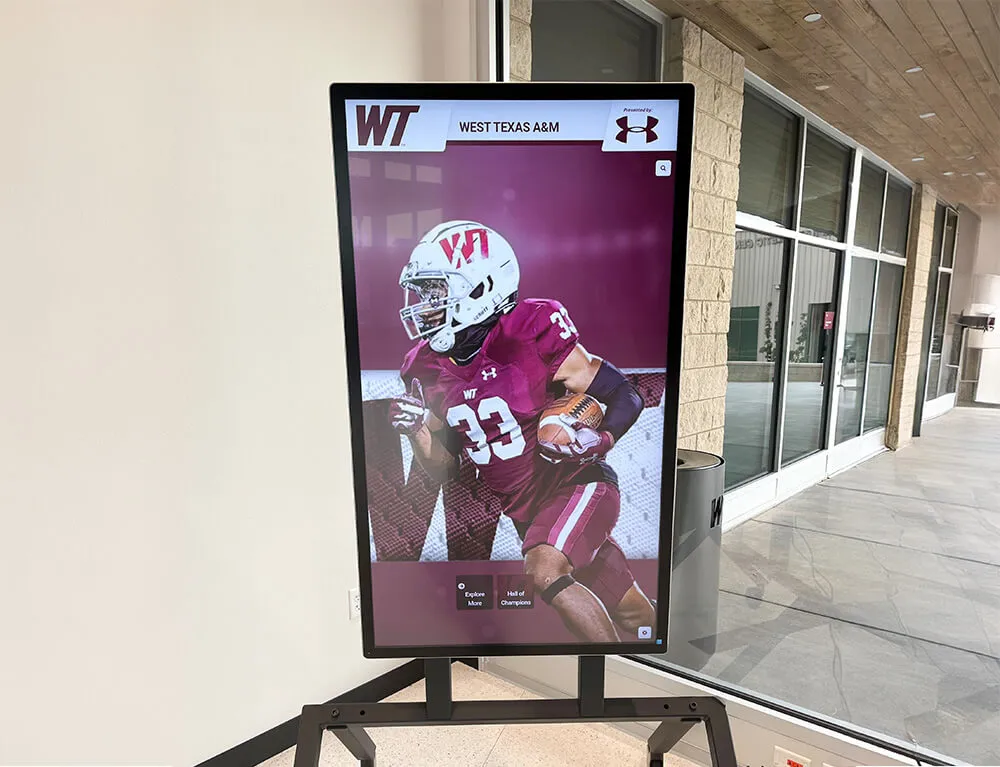
Digital recognition display solutions like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions provide commercial-grade touchscreen systems specifically designed for educational environments, featuring intuitive interfaces, robust content management platforms, reliable operation in high-traffic areas, and professional installation and ongoing support.
Strategic placement locations include main student centers or unions where students gather socially, career services office lobbies, academic building entrances in popular majors, athletic facilities and recreation centers, dining halls and cafeteria spaces, and residence hall common areas.

Web-Based Alumni Directories and Portals
Online platforms accessible through institutional websites provide anywhere, anytime access to alumni directories and mentorship matching systems.
Advantages include:
- Universal accessibility from any device with internet connection
- Personalized experiences with student accounts, saved searches, and mentorship history
- Integrated communication tools for messaging, video calls, and appointment scheduling
- Detailed search and filtering with unlimited criteria and sophisticated algorithms
- Easy updates allowing alumni to manage their own profiles without technical assistance
- Analytics and tracking providing detailed insights into usage patterns and program effectiveness
Leading platforms for 2025 include PeopleGrove offering AI-powered matching and “flash” mentoring for quick questions, Graduway providing fully branded digital communities combining directories with engagement tools, and specialized alumni management systems with mentorship modules integrated into broader relationship management platforms.
Mobile Applications
Dedicated mobile apps provide optimized experiences for smartphone users, which is increasingly how students prefer to access information and services.
Mobile-specific advantages include push notifications alerting students to mentor responses or relevant opportunities, location-based features suggesting nearby alumni for in-person meetings, quick access without navigating institutional websites, integration with device contacts and calendars, and offline access to saved profiles and resources.
Hybrid Approaches
The most comprehensive implementations combine physical touchscreen displays creating visibility and social discovery experiences with web and mobile platforms providing personalized, ongoing access and communication. This hybrid approach ensures that students encounter mentorship opportunities through multiple touchpoints while providing flexibility in how they ultimately engage with mentors.
Essential Features for Effective Discovery Boards
Regardless of platform format, certain features prove essential for facilitating meaningful student-alumni connections.
Robust Search and Filtering Capabilities
Students should be able to easily find relevant mentors through intuitive search including:
- Career field and industry (technology, healthcare, education, finance, nonprofit, etc.)
- Company type (corporate, startup, government, academic, entrepreneurial)
- Geographic location (hometown, current city, regions, international)
- Expertise areas (specific skills, knowledge domains, career transitions)
- Shared backgrounds (major, student organizations, athletics, demographics)
- Mentorship preferences (one-time advice, ongoing relationships, group mentoring)
- Availability and response time to manage student expectations
Advanced filtering allows students to narrow thousands of alumni profiles to the 10-20 most relevant mentors for their specific needs, dramatically lowering the barrier to initiating contact.
Compelling Alumni Profiles
Profile quality directly impacts student willingness to reach out. Effective profiles include:
- Professional headshots making alumni feel accessible and relatable
- Career trajectory timelines showing progression from graduation to current roles
- Current position and organization with brief descriptions
- Educational background including major, graduation year, and relevant experiences
- Mentorship availability clearly stating what guidance alumni can provide
- Areas of expertise highlighting specific knowledge or skills
- Personal connection points such as interesting hobbies, campus memories, or motivations for mentoring
- Video introductions (optional but highly effective) where alumni explain their career journey and mentorship approach
Showcasing alumni achievements through rich multimedia profiles demonstrates the diverse paths graduates pursue while making successful alumni feel approachable rather than intimidatingly accomplished.
Integrated Communication Systems
Effective discovery boards don’t just provide information—they facilitate action. Built-in communication features should include structured mentorship request forms prompting students to introduce themselves thoughtfully, messaging systems for ongoing conversations, video conferencing integration for virtual meetings, appointment scheduling tools, and connection history tracking so students and mentors can reference previous conversations.
By building these tools directly into discovery platforms, institutions reduce friction that causes students to abandon connection attempts when faced with figuring out how to contact alumni through external systems.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Current students benefit tremendously from seeing how mentorship has helped peers achieve their goals. Discovery boards should feature rotating testimonials from student mentees describing mentorship impact, alumni mentors sharing why they find the experience rewarding, specific examples of how connections led to internships or jobs, and video interviews with mentorship pairs discussing their relationships.

These stories serve multiple purposes: inspiring students to participate, providing models for effective mentorship relationships, recruiting additional alumni mentors, and documenting program impact for institutional leadership.
Resources and Guidance Content
Beyond facilitating connections, effective discovery boards provide educational content helping students and alumni engage productively including how to write effective mentorship requests, questions to ask mentors in initial conversations, goal-setting worksheets for mentorship relationships, professional communication guidelines and etiquette, industry-specific resources and career path information, and alumni-contributed advice articles and career insights.
By providing this scaffolding, institutions ensure that students feel prepared to make the most of mentorship opportunities rather than being overwhelmed by unstructured relationships they’re unsure how to navigate.
User Experience Design Considerations
The most feature-rich discovery board will fail if students find it confusing or difficult to use. Prioritize these user experience principles:
Intuitive Navigation
Students should be able to accomplish key tasks—searching for alumni, viewing profiles, and initiating contact—with minimal instruction through clear visual hierarchies, consistent navigation patterns, obvious calls-to-action, progress indicators for multi-step processes, and helpful tooltips or guidance for less obvious features.
Conduct usability testing with actual students before launch, observing where they encounter confusion or friction and iterating design based on their feedback rather than assumptions about what should work.
Mobile Responsiveness
With students increasingly accessing everything through smartphones, ensure discovery boards function flawlessly on small screens with touch-optimized interactions, readable text without zooming, properly sized tap targets, fast loading on cellular connections, and minimal data usage respecting limited student phone plans.
Accessibility Standards
Design for users with varying abilities by meeting WCAG 2.1 accessibility guidelines including screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation support, sufficient color contrast, alternatives to color-only information, and captions for video content.
Creating welcoming alumni spaces includes ensuring digital platforms are accessible to all students regardless of abilities or circumstances.
Privacy and Security
Students and alumni both need assurance that their information is protected through clear privacy policies explaining data usage, granular privacy controls allowing alumni to limit information sharing, secure messaging preventing external access to conversations, options to remain unlisted if alumni prefer passive participation, and compliance with relevant data protection regulations.
Implementing Your Student Mentorship Program: Step-by-Step
Technology platforms enable mentorship, but successful programs require thoughtful implementation addressing the human elements of matching, training, and ongoing support.
Step 1: Define Clear Program Objectives and Structure
Begin by establishing specific, measurable goals for your mentorship program using SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound) criteria. For example: “The goal of our mentoring program is to prepare students to enter the workforce and have 90% of senior-status program participants placed in a full-time job within 4 months of graduating.”
Additional objectives might include increasing first-year retention rates by a specific percentage, providing every interested student with at least one mentorship connection, engaging a target number of alumni in active mentorship roles, or achieving specific student satisfaction scores for career preparation.
Choose Your Program Structure
Effective mentorship programs can take several structural forms:
- Traditional one-on-one mentorship pairing individual students with individual alumni for ongoing relationships
- Group mentoring where one experienced alumnus mentors multiple students simultaneously
- Peer mentoring connecting upper-class students with first-years while alumni mentor seniors
- Flash mentoring offering quick 20-30 minute conversations for specific questions without ongoing commitments
- Project-based mentoring where alumni guide student teams on specific initiatives
- Industry panels bringing multiple alumni together for group discussions with students
Many successful programs incorporate multiple structures, recognizing that different students and alumni prefer different engagement models and that various formats serve different purposes throughout students’ developmental journeys.
Step 2: Recruit and Vet Alumni Mentors
The quality of your mentor pool directly determines program impact. Invest significant effort in recruiting committed, qualified alumni.
Effective Recruitment Strategies
Don’t assume alumni understand the benefits of mentoring—actively make the case through testimonial videos from current mentors describing the experience, data showing mentorship impact on student outcomes, clear explanations of time expectations and program structure, emphasis on flexibility and mentor control over involvement levels, and recognition strategies acknowledging mentor contributions.
Target alumni who have previously engaged with the institution through event attendance, volunteer roles, or donations, who work in fields where students express strong interest, who have explicitly indicated interest in mentoring or working with students, who graduated recently enough to remember student challenges vividly, and who represent diverse career paths, industries, and backgrounds reflecting student population diversity.
Leverage multiple recruitment channels including alumni newsletters and magazines, social media campaigns on LinkedIn and other platforms, alumni chapter meetings and regional events, direct outreach from career services or alumni relations staff, faculty recommendations of notable graduates in their fields, and student requests suggesting specific alumni they’d like to connect with.
Vetting and Onboarding
Maintaining program quality requires appropriate vetting processes including background checks if alumni will have unrestricted student access, review of professional credentials and current employment, assessment of mentoring motivations and expectations, and coordination with campus legal and student affairs offices ensuring policy compliance.
Provide clear onboarding explaining program goals and structure, mentor roles and boundaries, best practices for effective mentorship, communication protocols and available tools, privacy and confidentiality expectations, and how to handle concerning situations or challenging mentee questions.

Step 3: Match Mentors and Mentees Thoughtfully
Effective matching is both art and science, requiring attention to objective criteria and intangible compatibility factors.
Matching Criteria to Consider
- Career interests and goals aligning student aspirations with mentor expertise
- Industry and functional area matching specific fields and roles
- Geographic considerations prioritizing local mentors for students seeking in-person connections
- Communication preferences matching personalities and preferred interaction styles
- Shared backgrounds considering common experiences that build rapport
- Availability alignment ensuring time zone and schedule compatibility
- Specific expertise needs matching students facing particular challenges with relevant mentor experience
Modern platforms like PeopleGrove use AI-powered algorithms to suggest optimal matches based on profile analysis, but many programs successfully use simpler matching based on student requests and coordinator review of potential pairings.
Self-Matching vs. Assigned Matching
Programs typically use one of two matching approaches:
Self-selection where students browse discovery boards and initiate contact with alumni they find appealing offers advantages of student agency and ownership, natural alignment of interests and personalities, ongoing ability to connect with multiple mentors as needs evolve, and lower administrative burden on program coordinators.
Assigned matching where program staff pair students and mentors provides benefits of ensuring every participant gets matched rather than relying on student initiative, professional assessment of compatibility factors students might miss, guaranteed mentor engagement since alumni commit before knowing specific mentees, and structure helping students who feel overwhelmed by open-ended networking.
Many programs use hybrid approaches where formal matching creates initial pairings while discovery boards enable students to make additional connections independently.
Step 4: Provide Training and Ongoing Support
Even well-intentioned mentors and motivated mentees benefit from training and resources supporting productive relationships.
Mentor Training Topics
- Effective questioning techniques that prompt reflection rather than prescriptive advice
- Active listening skills and providing space for mentees to process
- Appropriate boundaries and referral protocols for issues beyond mentor scope
- Cultural competency and working with diverse mentees
- Setting expectations for relationship frequency and duration
- Specific challenges facing current students that might differ from mentors’ experiences
Mentee Training Topics
- How to prepare for mentorship conversations with clear goals and questions
- Professional communication standards including email etiquette and meeting punctuality
- Making the most of limited mentor time through focus and preparation
- Following up effectively and maintaining relationships over time
- When and how to seek additional mentors as needs evolve
- Expressing appreciation and giving back as future mentors
Ongoing Program Support
Beyond initial training, sustain engagement through monthly tips and conversation prompts sent to all participants, mid-program check-ins assessing relationship progress and addressing challenges, facilitated networking events bringing mentorship pairs together, recognition celebrations acknowledging mentor contributions, refresher training and advanced topics for experienced participants, and program staff availability for questions or concerns throughout the experience.
Step 5: Measure, Evaluate, and Continuously Improve
Demonstrating program value requires systematic evaluation while gathered data informs ongoing improvements.
Key Metrics to Track
Participation Metrics:
- Number of active mentor-mentee matches
- Student participation rates by class year, major, and demographic groups
- Alumni mentor recruitment and retention rates
- Average number of mentorship connections per student
- Program reach across student population
Engagement Quality Indicators:
- Frequency of mentor-mentee interactions
- Relationship duration and sustained engagement
- Student and mentor satisfaction ratings
- Discovery board usage analytics (searches, profile views, contact initiations)
- Completion rates for structured program elements
Outcome Measures:
- Student retention and graduation rates for participants vs. non-participants
- Job placement rates and time-to-employment after graduation
- Graduate school admission rates for participants
- Student confidence in career readiness (survey data)
- Alumni giving and volunteer engagement rates for mentor participants
Feedback Collection
Gather qualitative insights through post-program surveys from both students and mentors, focus groups exploring program strengths and improvement opportunities, testimonials and success stories documenting specific impacts, suggestion boxes for ongoing feedback, and regular reviews with program advisory committees including student and alumni representatives.
Act on feedback by implementing feasible suggestions and communicating changes to participants, explaining rationale when certain suggestions can’t be implemented, thanking contributors for input, and demonstrating that the program evolves based on participant experiences rather than remaining static.

Best Practices for Sustainable Mentorship Programs
Learning from established programs helps avoid common pitfalls while adopting proven strategies that drive long-term success.
Start Small and Scale Strategically
Rather than attempting to launch comprehensive programs serving all students immediately, pilot with a manageable cohort allowing refinement before expansion. Effective pilot approaches include focusing on senior students who need career guidance most urgently, targeting specific majors or schools within larger universities, recruiting a small group of highly committed alumni mentors for initial testing, or running intensive programs during specific time periods rather than year-round initially.
Document lessons learned during pilots thoroughly, gathering detailed feedback that informs full-scale implementation design and avoiding the temptation to prematurely expand before working out operational challenges.
Make Participation Flexible and Convenient
The primary barrier to alumni mentor participation is time constraints. Design programs respecting busy schedules through flexible communication formats letting mentors choose phone, video, email, or in-person meetings, realistic time expectations like one conversation monthly rather than weekly commitments, “micro-mentoring” options for quick questions without ongoing relationships, asynchronous options allowing mentors to respond when convenient rather than scheduled calls, and academic calendar awareness concentrating student outreach during school year rather than summer breaks.
Similarly, make student participation convenient by integrating mentorship into existing programs like career courses or capstone projects, offering academic credit for structured mentorship when appropriate, providing clear guidance reducing intimidation of networking with accomplished professionals, and eliminating unnecessary administrative barriers or complicated processes.
Recognize and Celebrate Mentor Contributions
Meaningful alumni recognition drives sustained engagement and recruits future mentors by demonstrating that institutions value volunteer contributions. Effective recognition strategies include featuring mentors on discovery boards and institutional websites, sending personalized thank-you communications from institutional leadership, hosting annual appreciation events celebrating mentor impact, providing LinkedIn recommendations or professional references for mentor volunteers, and showcasing mentor profiles in alumni publications and social media.
Physical recognition through digital displays prominently featuring active mentors creates visible appreciation while inspiring other alumni to participate when they see peers highlighted for meaningful contribution.
Create Community Among Participants
Mentorship programs succeed when they build communities rather than just facilitating isolated one-on-one relationships. Foster community through networking events bringing together multiple mentorship pairs, online forums where mentors share insights and students ask questions, mentor orientation sessions creating cohorts with shared experiences, student mentee cohorts meeting regularly to discuss their mentorship experiences and career development journeys, and alumni mentor networks facilitating professional connections among mentors themselves.
These community elements provide social reinforcement, shared learning, and sense of belonging that sustain participation beyond individual mentorship relationships.
Leverage Technology Appropriately
While platforms enable mentorship at scale, avoid over-reliance on technology at the expense of human connection. Use technology for tasks it handles well including facilitating discovery and initial matching, scheduling and logistical coordination, content delivery and resource sharing, data collection and program analytics, and communication documentation. Preserve human elements for relationship building, nuanced guidance requiring conversation, celebrating milestones and achievements, addressing challenges or concerns, and sustaining motivation and commitment over time.
Interactive alumni platforms work best when they reduce friction enabling human connections rather than attempting to replace personal interaction with automated systems.
Integrating Discovery Boards with Physical Campus Spaces
While online platforms provide essential functionality, physical touchscreen displays create unique opportunities for discovery and engagement integrated into students’ daily campus experiences.
Strategic Placement for Maximum Impact
Location dramatically affects discovery board utilization. Prioritize high-traffic areas where students naturally congregate including main entrances to student centers, career services office lobbies and waiting areas, popular academic building entrances, dining halls and cafeteria spaces, recreation centers and athletic facilities, residence hall common areas, and library entrances and study spaces.
Consider student flow patterns throughout typical days, placing displays where students have dwell time to explore rather than locations where they’re rushing past.
Creating Engaging Discovery Experiences
Physical displays should leverage their unique strengths compared to web platforms through large-format visuals showcasing compelling alumni stories and achievements, social discovery enabling groups of students to explore together, serendipitous exposure reaching students not actively seeking mentorship, multimedia content including video profiles and career path visualizations, and touchscreen interaction creating engaging, tactile experiences more memorable than passive viewing.
Solutions from Rocket Alumni Solutions provide intuitive interfaces designed specifically for casual users without training, featuring prominent search functionality, featured alumni rotations highlighting diverse career paths, quick response codes enabling students to save profiles or continue exploring on personal devices, and content management systems allowing easy updates without technical expertise.
Coordinating Physical and Digital Experiences
The most effective implementations create seamless experiences across physical and digital touchpoints. When students discover interesting alumni on physical displays, provide easy transitions to online platforms through QR codes linking to full profiles, text-to-download prompts for mobile apps, save functionality sending information to student email, and clear instructions for accessing the web portal.
Conversely, promote physical displays through online platforms by featuring their locations on websites and apps, highlighting new content installations in student emails, and creating social media content showcasing students using displays.
Overcoming Common Mentorship Program Challenges
Even well-designed programs encounter predictable challenges. Anticipating these issues and implementing proactive solutions prevents problems from undermining program effectiveness.
Challenge: Low Student Participation
Causes: Students may not be aware of the program, feel intimidated by networking with accomplished professionals, be uncertain what to ask or how to benefit, or lack time for additional commitments.
Solutions: Integrate mentorship program promotion into student orientation, advising sessions, and career courses; partner with student organizations for peer promotion; feature compelling student testimonials demonstrating accessible, positive experiences; provide clear guidance on preparing for mentorship conversations; emphasize flexible, low-time-commitment options; and make discovery boards highly visible in daily student pathways.
Challenge: Mentor Ghosting or Inconsistent Engagement
Causes: Alumni sign up with good intentions but face unexpected work demands, unclear expectations lead to uncommitted participation, or poor matching creates relationships that don’t resonate.
Solutions: Set clear expectations during recruitment about realistic time commitments; provide multiple engagement level options from intensive to minimal; check in with mentors proactively offering support or adjustments; implement mentorship agreements formalizing mutual commitments; and make it acceptable for mentors to pause participation rather than disappearing.
Challenge: Poor Quality Matches Leading to Disappointing Experiences
Causes: Matching based solely on career field overlooks personality compatibility, students don’t clearly articulate their needs, or mentors lack experience with current student challenges.
Solutions: Collect detailed information about communication preferences and personalities; allow students to review multiple potential matches before committing; facilitate initial “chemistry check” conversations before formal pairing; provide clear pathways to request different mentors if initial matches don’t work; and continuously refine matching algorithms based on successful relationship characteristics.
Challenge: Difficulty Measuring Long-Term Impact
Causes: Student outcomes unfold over years after graduation, attribution is challenging when multiple factors influence success, and longitudinal tracking requires sustained effort.
Solutions: Establish baseline metrics before program launch for comparison; conduct regular surveys of participants tracking confidence, satisfaction, and intermediate outcomes; maintain contact with graduates through alumni association systems; document specific instances where mentorship directly enabled opportunities; and track leading indicators like student engagement and career preparation confidence that predict later success.
The Future of Student-Alumni Mentorship Platforms
As technology evolves and generational expectations shift, student-alumni mentorship platforms continue advancing with new capabilities and approaches.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Matching
AI algorithms analyze multiple data points to suggest optimal mentor-mentee pairings considering factors like communication style compatibility, career trajectory similarities, personality complementarity, likelihood of sustained engagement, and prediction of relationship success based on historical patterns from previous matches.
While human oversight remains essential, AI augmentation enables scaling programs to thousands of participants while maintaining quality matching that would be impossible through manual processes alone.
Virtual Reality for Immersive Career Exploration
Emerging platforms enable students to explore career environments through virtual reality experiences guided by alumni, tour workplaces and observe typical days in various professions, participate in simulated professional scenarios with real-time alumni coaching, and attend virtual networking events feeling more present than video calls.
These immersive experiences particularly benefit students without travel resources to visit diverse workplaces or those exploring careers unfamiliar to their social networks.
Integration with Learning Management Systems
Increasingly, mentorship platforms integrate with institutional LMS systems allowing career development courses to incorporate structured mentorship requirements, faculty to track student mentorship engagement as program participation metrics, career exploration assignments directing students to discovery boards, and mentorship documentation contributing to digital portfolios or career readiness credentials.
This integration embeds mentorship in formal educational experiences rather than positioning it as optional supplementary programming.
Mobile-First Design and Micro-Interactions
Recognizing that students increasingly engage through smartphones during brief moments throughout days, platforms optimize for quick, valuable micro-interactions like five-minute flash conversations answering specific questions, push notification prompts to check in with mentors, brief video messages replacing longer synchronous calls, and bite-sized career advice content consumable while commuting or between classes.
These approaches respect limited attention spans and fragmented time availability while maintaining relationship continuity through frequent small touchpoints rather than infrequent extended conversations.
Conclusion: Transforming Student Success Through Alumni Connection
The evidence supporting mentorship’s impact is compelling and consistent: students with mentors graduate at higher rates, secure employment more successfully, demonstrate greater confidence and satisfaction, and develop professional networks that benefit them throughout careers. Alumni mentors gain professional fulfillment, skill development, expanded networks, and deeper connections with institutions that shaped their trajectories. Institutions benefit from improved student outcomes, strengthened alumni engagement, enhanced reputation, and distinctive programming that differentiates them in competitive markets.
Successful implementations combine thoughtful program design addressing the human elements of matching, training, recognition, and support with technology platforms that facilitate rather than replace personal connection. Whether through sophisticated web applications, dedicated mobile apps, or physical touchscreen displays creating campus touchpoints, effective discovery boards make it easy for students to find relevant mentors and take action on those connections without the intimidation and uncertainty that prevent many from networking independently.
Solutions like digital recognition displays from Rocket Alumni Solutions provide institutions with powerful tools for showcasing alumni achievements while facilitating mentorship connections through interactive touchscreen experiences that engage students where they already spend time. These platforms transform physical spaces into networking hubs while providing the robust search, rich multimedia profiles, and integrated communication tools that enable meaningful student-alumni relationships at scale.
Ready to Launch Your Student-Alumni Mentorship Program?
Discover how digital recognition displays and alumni discovery boards can transform student success and alumni engagement at your institution. Explore Rocket Alumni Solutions to see how schools and universities nationwide are using interactive touchscreen technology to connect students with alumni mentors, showcase graduate achievements, and create campus touchpoints that strengthen institutional communities through meaningful intergenerational relationships.
From facilitating career connections to celebrating alumni accomplishments, the right digital platforms make it easier to implement mentorship programs that improve student outcomes, deepen alumni engagement, and build traditions of giving back that sustain institutions for generations to come.