Key Takeaways
Discover how to build effective cybersecurity trainee recognition programs that improve retention, boost morale, and create strong security cultures. Comprehensive guide with real strategies for IT and security leaders.
The Cybersecurity Talent Challenge
The cybersecurity industry faces unprecedented workforce challenges. According to research from (ISC)², the global cybersecurity workforce gap represents millions of unfilled positions, with demand far outpacing supply. Organizations struggle not only to recruit qualified candidates but to retain talented professionals once hired.
Cybersecurity trainees and early-career professionals face unique pressures that contribute to high turnover:
- Overwhelming Learning Curve: Constant pressure to master new technologies, threats, and defensive techniques
- High-Stress Environment: Responsibility for protecting critical systems creates significant psychological pressure
- Always-On Demands: Security incidents require 24/7 availability creating work-life balance challenges
- Imposter Syndrome: Feeling inadequately prepared despite training and education
- Limited Recognition: Security work often goes unnoticed when successful—only failures receive attention
- Unclear Career Paths: Difficulty understanding advancement opportunities and progression timelines

Recognition programs specifically addressing these challenges create work environments where cybersecurity trainees feel valued, supported, and motivated to build long-term careers rather than seeking opportunities elsewhere.
Benefits of Cybersecurity Trainee Recognition Programs
Enhanced Retention and Reduced Turnover
The most compelling benefit of recognition programs addresses the critical retention challenge. Organizations implementing comprehensive recognition practices report significantly lower voluntary turnover compared to those without formal recognition.
💰 Reduced Replacement Costs
Turnover costs in cybersecurity range from $100,000-$200,000 per position when accounting for recruitment, training, and productivity losses during vacancy periods
📈 Institutional Knowledge Retention
Long-tenured security professionals develop deep understanding of organizational systems, threats, and vulnerabilities that cannot be quickly replaced
🎯 Improved Team Cohesion
Stable teams develop stronger collaboration, communication, and incident response capabilities compared to teams experiencing frequent turnover
🔒 Enhanced Security Posture
Experienced security professionals identify threats faster and respond more effectively than newly hired replacements
For organizations facing continuous recruitment challenges, recognition programs represent strategic investments in workforce stability. Solutions like employee recognition displays create visible celebration of security team contributions that reinforce organizational commitment to valuing security professionals.

Increased Motivation for Continuous Learning
Cybersecurity requires continuous learning to stay current with evolving threats, technologies, and defensive strategies. Recognition programs that celebrate educational achievements and skill development create cultures that encourage ongoing professional growth:
Certification Recognition
- Celebrate completion of major certifications (CISSP, CEH, OSCP, Security+, etc.)
- Acknowledge preparation effort and study dedication
- Provide financial bonuses or salary increases tied to certification achievement
- Display certifications prominently in team areas and organizational communications
- Share achievement announcements with leadership and across the organization
Skills Development Milestones
- Recognize completion of training programs and courses
- Honor achievement of technical skill benchmarks
- Celebrate participation in capture-the-flag competitions and exercises
- Acknowledge contributions to internal knowledge bases and documentation
- Highlight presentation of training sessions or lunch-and-learn programs
When trainees see colleagues recognized for achieving certifications or mastering new skills, they receive clear messages about what the organization values and supports. This creates positive peer pressure encouraging professional development while demonstrating concrete career advancement pathways.
Reduced Burnout and Improved Well-Being
Cybersecurity professionals experience burnout at higher rates than many other technology roles due to constant threat pressure and high-stakes responsibility. Recognition programs addressing well-being create protective factors against burnout:
- Validation of Efforts: Acknowledging the difficulty and importance of security work helps professionals feel their efforts matter
- Work-Life Balance Recognition: Celebrating professionals who maintain sustainable work patterns rather than excessive overtime
- Team Support Appreciation: Recognizing mutual support behaviors and collaborative problem-solving
- Progress Acknowledgment: Celebrating incremental improvements and small wins rather than only major achievements
- Mental Health Support: Normalizing discussions about stress management and wellness
- Positive Feedback: Providing regular positive reinforcement in field where negative feedback dominates

Organizations implementing recognition programs focused on sustainable practices and well-being report improved morale, reduced stress indicators, and lower burnout rates compared to teams without such programs.
Attraction of Quality Candidates
Recognition programs benefit not only current employees but recruitment efforts. Organizations known for valuing and recognizing security professionals attract higher quality candidates:
Employer Brand Enhancement: Public recognition of security team achievements through organizational communications, social media, and industry participation creates visibility for security programs.
Candidate Assessment Tool: Discussing recognition programs during interviews provides insight into organizational culture and values.
Competitive Differentiation: In competitive talent markets, robust recognition programs differentiate organizations from competitors offering only compensation.
Referral Generation: Satisfied security professionals refer qualified candidates when they feel valued and recognized.
Organizations establishing corporate recognition walls or interactive displays celebrating security team achievements create tangible evidence of organizational commitment that resonates with prospective candidates during interviews and facility tours.

Essential Components of Cybersecurity Recognition Programs
Clear Recognition Criteria and Categories
Effective recognition programs establish transparent criteria defining what achievements warrant recognition. This ensures consistency, fairness, and understanding across the security team:
Recognition Categories for Security Teams
Technical Excellence
- Security certifications earned (all levels from entry to advanced)
- Vulnerability discoveries in internal systems or applications
- Development of security tools or automation
- Successful incident response and threat mitigation
- Security architecture contributions and design improvements
- Penetration testing accomplishments and findings
Professional Development
- Completion of training programs and courses
- Conference presentations and speaking engagements
- Published research papers or blog posts
- Participation in professional organizations
- Mentorship of junior security professionals
- Contribution to open-source security projects
Team Contribution
- Knowledge sharing and documentation creation
- Cross-functional collaboration and partnership
- Security awareness training delivery
- Process improvement initiatives
- Exceptional peer support and assistance
- Positive team culture contributions
Values Demonstration
- Ethical behavior and integrity in security practices
- Customer-focused security solutions
- Innovation in approach to security challenges
- Proactive identification of emerging threats
- Commitment to continuous improvement
- Leadership demonstration regardless of title
Organizations should customize recognition categories to align with specific security program goals, organizational values, and team priorities. The key is ensuring criteria remain transparent, achievable, and meaningful to security professionals.
Multiple Recognition Methods and Formats
Comprehensive recognition programs utilize diverse methods addressing different preferences and achievement types:

Recognition Formats
- Public Acknowledgment: Team meetings, all-hands presentations, organizational newsletters
- Physical Recognition: Certificates, plaques, trophies for major achievements
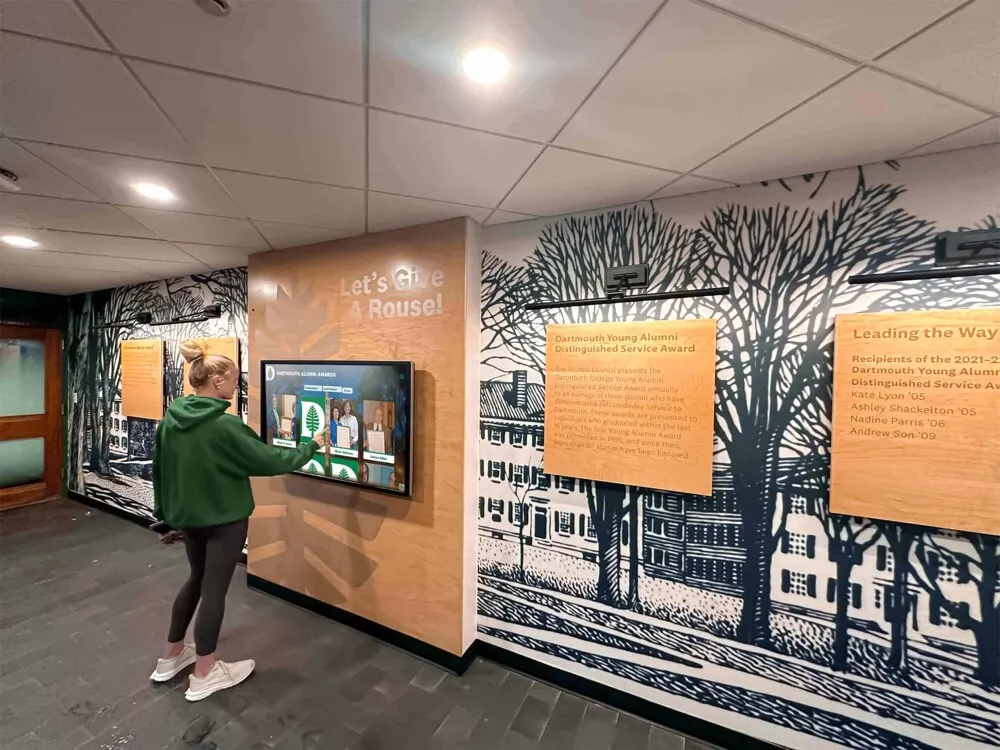
- Digital Displays: Interactive touchscreens showcasing security team accomplishments
- Professional Development: Conference attendance, training budgets, certification support
- Monetary Rewards: Bonuses, salary increases, gift cards aligned with achievements
- Time-Off Awards: Additional PTO or flexible scheduling for major accomplishments
- Career Advancement: Promotions, expanded responsibilities, leadership opportunities
- Peer Recognition: Colleague nominations and appreciation programs
Different recognition formats resonate with different individuals. Some professionals value public acknowledgment while others prefer private recognition. Effective programs offer variety ensuring all team members receive recognition in formats meaningful to them.
Transparent Nomination and Selection Processes
Recognition programs only succeed when perceived as fair and inclusive. Establishing transparent processes prevents perceptions of favoritism or bias:
Multiple Nomination Channels: Allow self-nominations, manager nominations, peer nominations, and automated recognition for objective achievements like certifications.
Clear Evaluation Criteria: Publish detailed descriptions of what qualifies for each recognition category with specific examples and standards.
Diverse Review Committees: Include multiple perspectives in recognition decisions rather than single-person determinations.
Regular Recognition Cadence: Establish consistent schedules (monthly, quarterly, annually) rather than ad-hoc recognition creating perception of randomness.
Appeal Mechanisms: Provide pathways for questioning recognition decisions when concerns about fairness arise.
Demographic Monitoring: Track recognition patterns ensuring all groups receive proportional acknowledgment without systematic exclusion.
Organizations implementing staff recognition displays should ensure nomination processes support the visibility created by displays—combining transparent selection with public celebration.

Implementation Strategies for Security Teams
Phase 1: Program Planning and Design
Recognition Program Development Process
Assess Current State
Survey security team about recognition preferences, gaps, and what motivates them professionally

Define Program Goals
Establish specific objectives for recognition program including retention targets, engagement improvements, and culture outcomes

Design Recognition Framework
Create recognition categories, criteria, nomination processes, and selection methods with input from security team

Secure Budget and Resources
Determine program costs including displays, awards, professional development funding, and administrative time

Develop Communication Plan
Create launch communications explaining program purpose, processes, and participation methods

Pilot and Refine
Test recognition program with small group before full deployment, gathering feedback for improvements

Phase 2: Program Launch and Rollout
Executive Sponsorship: Security recognition programs require visible support from leadership demonstrating organizational commitment. CISO or IT leadership should publicly champion recognition initiatives.
Comprehensive Training: Managers need training on recognition best practices, nomination processes, and how to leverage recognition for team engagement and retention.
Initial Recognition Content: Plan first recognition announcements showcasing diverse achievements across the security team—demonstrating inclusive recognition from program inception.
Multi-Channel Communication: Announce program through team meetings, email communications, intranet posts, and one-on-one discussions ensuring all team members understand participation methods.
Celebration Launch Event: Consider hosting recognition ceremony or team event celebrating program launch and first honorees.
Critical Launch Success Factors
- Clear explanation of recognition criteria and processes
- Easy-to-use nomination submission methods
- Visible leadership participation and support
- Early recognition of diverse team members
- Connection to career development opportunities
- Feedback mechanisms for program improvement
- Regular communication about program updates

Phase 3: Ongoing Management and Optimization
Consistent Recognition Cadence: Maintain regular recognition schedules rather than sporadic acknowledgment. Monthly or quarterly recognition ceremonies create predictable celebration opportunities.
Diverse Recognition Distribution: Monitor who receives recognition ensuring all team members—regardless of role, tenure, or specialty—receive appropriate acknowledgment for contributions.
Metric Tracking: Measure program effectiveness through retention rates, engagement surveys, participation levels, and feedback quality.
Continuous Improvement: Gather regular feedback about recognition program effectiveness and make adjustments based on team input and changing needs.
Recognition Integration: Connect recognition displays and programs with performance reviews, career development discussions, and succession planning processes.
Organizations implementing digital recognition displays benefit from easy content updates allowing regular addition of new achievements without production delays or printing costs—supporting consistent recognition cadences.
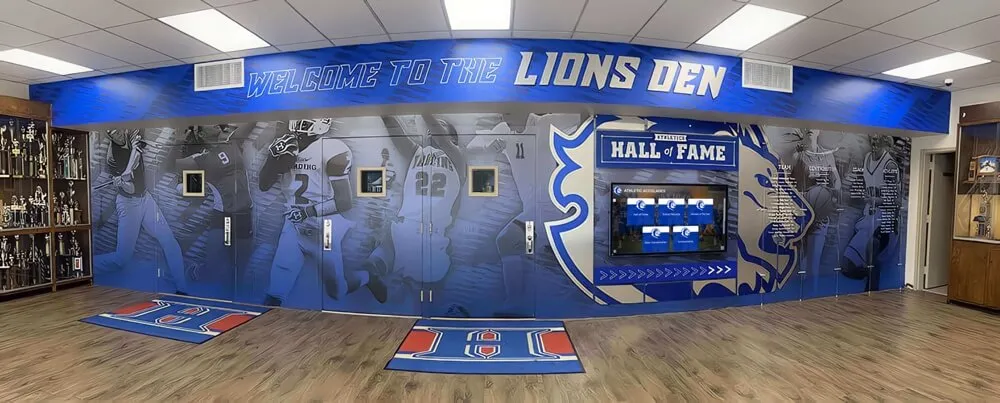
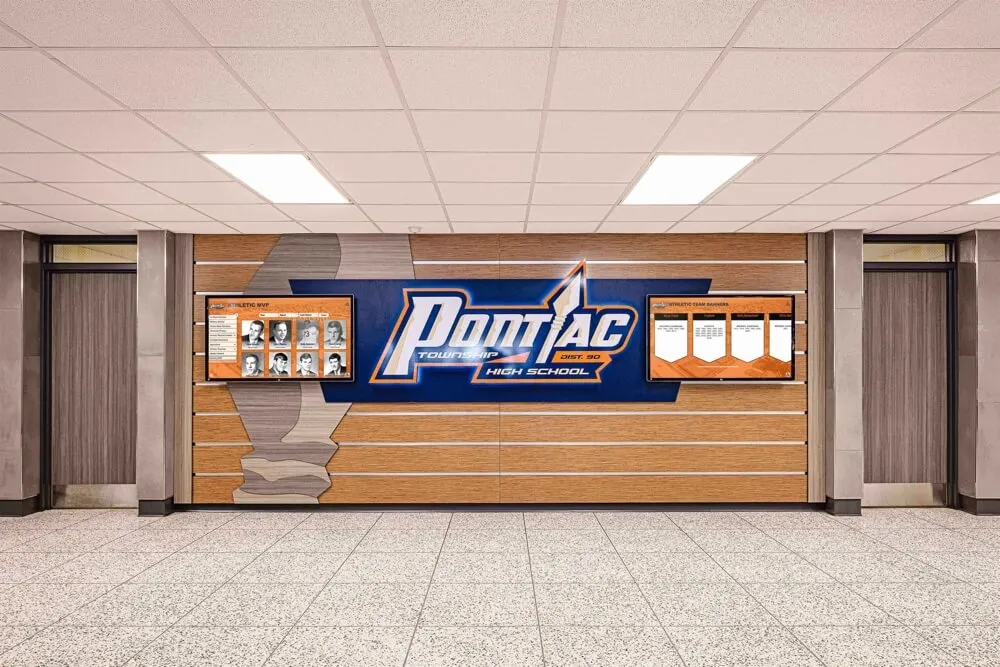
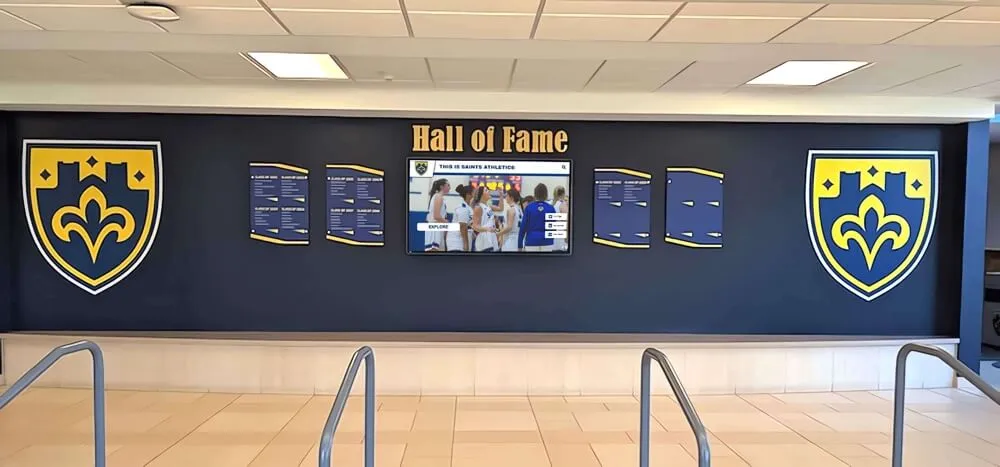
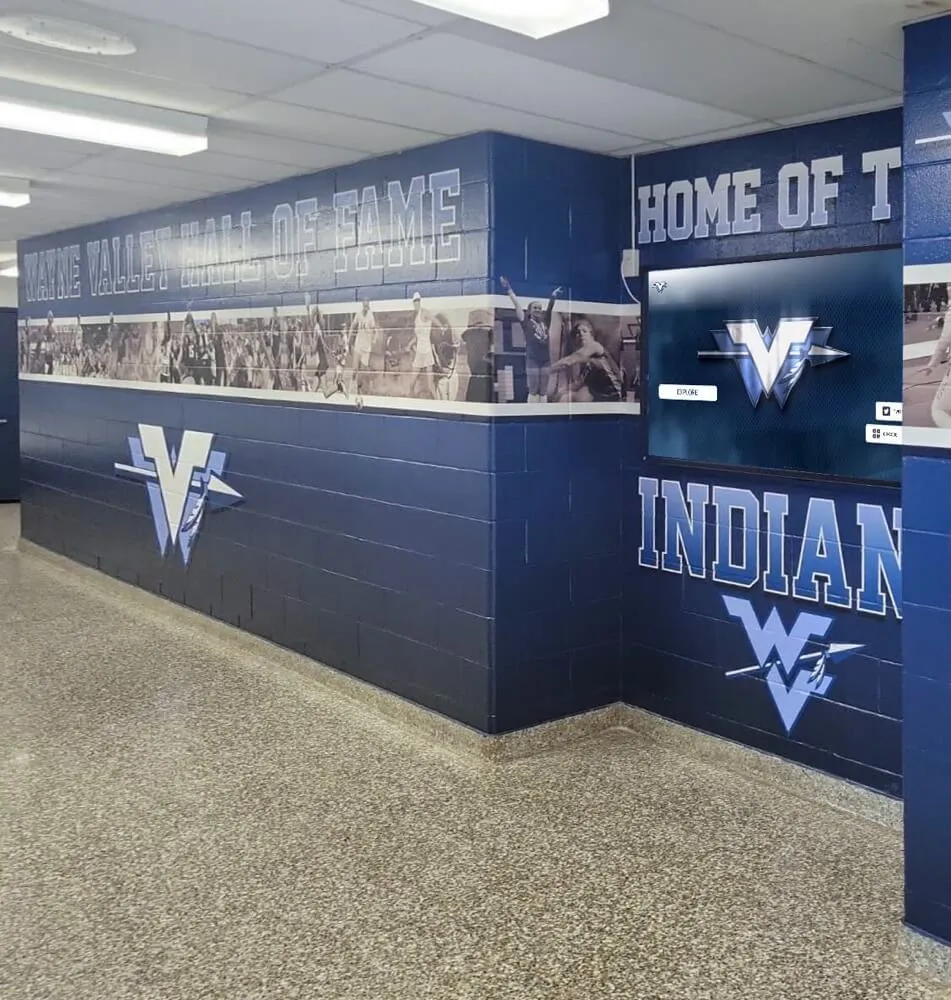
Recognition Display Solutions for Security Teams
Traditional Recognition Approaches
Physical recognition displays provide tangible acknowledgment of cybersecurity team achievements:
Certification Walls: Display frames showcasing security certifications earned by team members, updated as new certifications are achieved.
Achievement Boards: Cork boards or display cases featuring certificates, award plaques, and recognition documentation.
Trophy Cases: Glass-enclosed displays housing physical awards and recognition items.
While traditional approaches provide physical presence, they face limitations including space constraints, difficult updates requiring manual intervention, and inability to showcase rich multimedia content or detailed achievement stories.
Digital Recognition Display Advantages
Modern Recognition Technology
Digital recognition displays transform how organizations celebrate security team achievements through interactive technology:
Key Capabilities
- Unlimited Capacity: Recognize hundreds of team members and achievements without space constraints
- Rich Profiles: Include photos, certification details, career progression, project highlights, and video content
- Easy Updates: Add new recognitions instantly through web-based content management
- Interactive Search: Team members search for colleagues by name, certification, or achievement type
- Remote Access: Distributed team members view recognition online from anywhere
- Analytics: Track engagement metrics showing which content resonates most
- Integration: Connect with HR systems, learning platforms, and credential management tools
Implementation Considerations
- Screen size appropriate for viewing distance (43"-75" typical)
- Installation location in security operations center or IT department area
- Network connectivity for content updates and management
- Content management training for administrators
- Integration with existing recognition workflows
- Accessibility compliance for all users
- Branding alignment with organizational identity
- Budget for hardware, software, and ongoing maintenance
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built platforms designed specifically for recognition applications, offering advantages over generic digital signage not optimized for celebrating achievements and career development.
Organizations implementing touchscreen kiosk software designed for recognition benefit from features specifically supporting employee celebration rather than adapting general-purpose signage platforms.
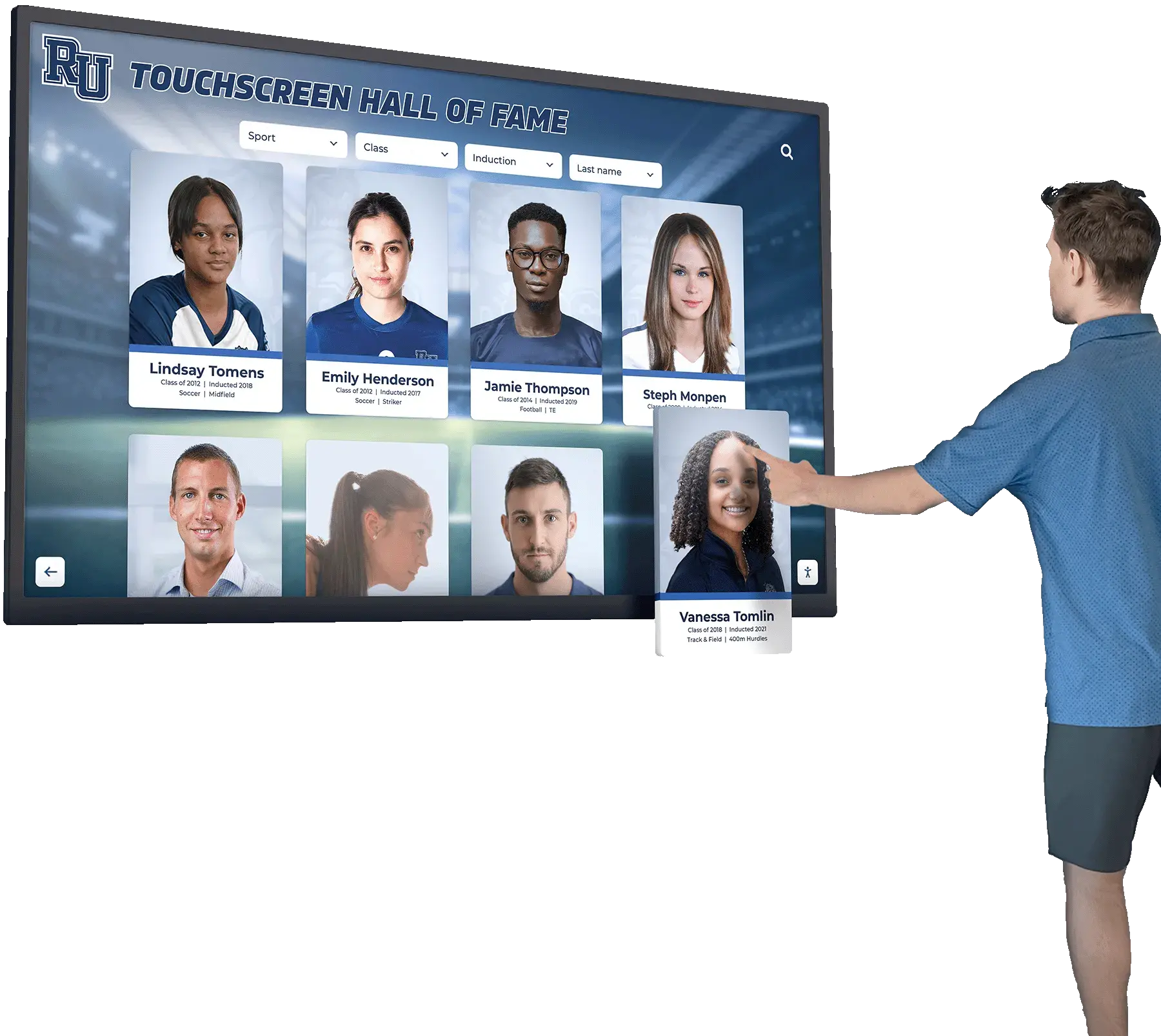
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Recognition
Balance Individual and Team Recognition
Security work requires both individual expertise and collaborative teamwork. Effective recognition programs celebrate both:
Individual Achievements: Certifications earned, technical innovations, vulnerability discoveries, research contributions, and personal professional development demonstrate individual excellence.
Team Accomplishments: Successful incident responses, project completions, security program implementations, and collaborative problem-solving showcase team effectiveness.
Balancing individual and team recognition prevents perception that only individual contributors receive acknowledgment while maintaining motivation for personal excellence.
Connect Recognition to Career Development
Recognition as Career Pathway Visibility
The most powerful recognition programs connect acknowledgment to clear career advancement opportunities:
Career Progression Demonstration
- Showcase career journeys of security professionals from entry-level to senior positions
- Highlight certifications and skills required for advancement
- Display timelines showing typical progression pathways
- Feature mentorship relationships and sponsorship
- Connect recognition achievements to promotion requirements
Professional Development Support
- Tie recognition to training budget allocations
- Award conference attendance for achievement
- Provide study time and resources for certification preparation
- Offer tuition reimbursement for degree programs
- Support participation in professional organizations
When trainees see direct connections between recognition and career advancement, they understand concrete pathways to progress—reducing uncertainty about how to build security careers within the organization.
Emphasize Values and Behavior Recognition
While technical achievement matters, behavioral recognition reinforces desired security culture:
Ethical Behavior: Recognize professionals who demonstrate integrity, transparency, and ethical decision-making in security practices.
Customer Focus: Acknowledge security professionals who balance security requirements with user experience and business enablement.
Collaboration: Celebrate partnership behaviors, knowledge sharing, and cross-functional teamwork.
Innovation: Recognize creative approaches to security challenges and willingness to experiment with new defensive strategies.
Continuous Learning: Honor commitment to staying current with evolving threats, technologies, and best practices.
Values-based recognition creates security cultures focused not just on technical capability but on behaviors that make security programs successful and sustainable long-term.
Maintain Consistent Recognition Frequency

Recognition Cadence Best Practices
- Weekly Recognition: Informal peer-to-peer appreciation in team meetings
- Monthly Recognition: Manager acknowledgment of recent achievements and contributions
- Quarterly Recognition: Formal recognition ceremonies celebrating major accomplishments
- Annual Recognition: Year-end awards honoring sustained excellence and career milestones
- Real-Time Recognition: Immediate acknowledgment of exceptional incident response or critical contributions
Consistent recognition frequency ensures team members receive regular acknowledgment rather than occasional, sporadic celebration creating perception that recognition occurs randomly.
Measuring Recognition Program Effectiveness
Key Performance Indicators
Track specific metrics demonstrating recognition program impact:
Retention Metrics
- Voluntary turnover rates in security team before and after program implementation
- Average tenure of security professionals
- Exit interview data mentioning recognition or lack thereof
- Retention rates of high performers versus average performers
Engagement Indicators
- Employee engagement survey scores related to recognition and appreciation
- Participation rates in nomination and peer recognition processes
- Recognition display interaction frequency (for digital systems)
- Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) tracking
Professional Development Measures
- Certification achievement rates year-over-year
- Training program completion percentages
- Conference attendance and speaking engagement participation
- Internal knowledge sharing and mentorship activity
Culture Assessments
- Team collaboration and communication quality
- Innovation and experimentation frequency
- Work-life balance and burnout indicators
- Psychological safety and trust measures
ROI Calculation Framework
| Metric | Baseline | Post-Implementation | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Turnover Rate | 25% | 15% | 10% reduction = 2-3 fewer replacements |
| Cost per Replacement | $150,000 | $150,000 | Savings: $300,000-$450,000 |
| Program Investment | - | $50,000 | Annual program cost |
| Net ROI | - | - | 500-800% return on investment |
Organizations implementing comprehensive recognition programs typically achieve break-even within first year while gaining retention and culture benefits that compound over time.
Qualitative Feedback Collection
Quantitative metrics provide important data, but qualitative feedback offers deeper understanding:
Regular Surveys: Conduct brief pulse surveys asking security team members about recognition program effectiveness, fairness, and meaningfulness.
Focus Groups: Host small group discussions exploring recognition experiences, preferences, and suggestions for improvement.
One-on-One Interviews: Conduct individual conversations with team members at various tenure levels gathering detailed feedback.
Exit Interviews: Ask departing employees about recognition experiences and whether improved recognition would have influenced retention decisions.
New Hire Feedback: Survey recently hired security professionals about how recognition program influenced their decision to join organization.
Organizations implementing interactive recognition displays can track engagement analytics showing which recognition content receives most views while combining quantitative data with qualitative feedback about program impact.
Special Considerations for Remote and Hybrid Security Teams
Virtual Recognition Strategies
Distributed security teams require recognition approaches that work across locations and time zones:
Remote Recognition Best Practices
- Digital-First Approaches: Prioritize online recognition platforms accessible from anywhere rather than physical displays only available in headquarters
- Video Recognition: Record recognition messages from leadership and colleagues for asynchronous viewing
- Virtual Ceremonies: Host recognition events via video conference with interactive elements
- Slack/Teams Integration: Announce recognition in communication platforms where teams already collaborate
- Time Zone Consideration: Schedule recognition events at times accessible across global team locations
- Shipped Recognition Items: Mail physical awards, certificates, or gift cards to remote team members
- Online Galleries: Create web-based recognition displays viewable from anywhere

The shift to remote and hybrid work makes digital recognition solutions increasingly essential. Physical displays in headquarters only reach fraction of distributed teams, while online platforms ensure all team members regardless of location receive equal recognition visibility.
Equity Across Location and Work Arrangement
Recognition programs must ensure remote workers receive equal acknowledgment to on-site employees:
Visibility Monitoring: Track recognition distribution by location ensuring remote team members aren’t systematically under-recognized.
Remote-Friendly Criteria: Ensure recognition categories don’t inadvertently favor on-site employees through criteria like “office presence” or casual collaboration metrics easier to observe in physical locations.
Multiple Nomination Channels: Provide nomination methods accessible to distributed teams rather than requiring physical presence.
Manager Training: Educate managers about proximity bias—the tendency to preferentially recognize employees physically present—and strategies to mitigate it.
Rotation of Recognition Events: Alternate recognition event times accommodating different time zones rather than consistently scheduling during single location’s business hours.
Budget Planning for Recognition Programs
Cost Components and Investment Levels
Recognition programs can be implemented at various investment levels based on organizational size and resources:
Recognition Program Budget Tiers
Essential Program: $5,000-$15,000
- Formal recognition policy and criteria documentation
- Certificates and small awards
- Basic recognition ceremony budgets
- Modest professional development support
- Simple bulletin board or display area
- Internal communication about achievements
Comprehensive Program: $20,000-$50,000
- Digital recognition display system
- Substantial certification and training funding
- Conference attendance awards
- Recognition event budgets
- Monetary bonuses and gift awards
- Dedicated recognition program management
- Integration with HR and learning systems
Advanced Program: $50,000+
- Multiple digital display locations
- Extensive professional development budgets
- Significant monetary awards
- Sabbatical or special project opportunities
- Advanced career coaching and mentorship
- Comprehensive analytics and reporting
- Full-time program management resources
Organizations should start with essential programs establishing recognition foundations before expanding to more comprehensive approaches as programs demonstrate value and gain organizational support.
Return on Investment Justification
When proposing recognition program budgets to leadership, emphasize measurable returns:
Turnover Cost Savings: Calculate costs of replacing security professionals (recruitment, training, productivity loss) and demonstrate how even modest retention improvements generate substantial savings exceeding program investment.
Productivity Improvements: Research shows recognized employees demonstrate higher productivity, engagement, and discretionary effort—quantify these benefits using industry benchmarks.
Recruitment Efficiency: Organizations known for strong recognition cultures fill positions faster with higher quality candidates—reduce time-to-hire costs and recruitment expenses.
Security Posture Enhancement: Experienced, stable security teams identify and respond to threats more effectively than teams experiencing high turnover—quantify incident response improvements and vulnerability reduction.
Employer Brand Value: Strong recognition programs enhance organizational reputation in competitive talent markets—difficult to quantify precisely but valuable for long-term talent attraction.
Most organizations implementing comprehensive recognition programs achieve return on investment within 12-18 months while building cultural assets that deliver compounding benefits over time.

Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Manager Resistance or Inconsistency
Some managers resist recognition programs or apply them inconsistently creating equity concerns:
Solution: Provide comprehensive manager training explaining recognition program benefits, processes, and expectations. Include recognition frequency in manager performance metrics. Share data about retention and engagement improvements in teams with strong recognition practices versus those without. Offer recognition templates and examples making participation easier.
Challenge: Perception of Favoritism
Poorly managed recognition programs can create perceptions that only certain team members receive acknowledgment:
Solution: Establish transparent nomination and selection processes with clear criteria. Use diverse review committees rather than single-person decisions. Monitor recognition distribution patterns identifying potential bias. Provide multiple recognition channels including peer nominations. Regularly communicate recognition statistics demonstrating broad participation.
Challenge: Limited Budget Constraints
Organizations with tight budgets struggle to fund comprehensive recognition programs:
Solution: Start with low-cost recognition approaches including peer recognition, public acknowledgment, and non-monetary rewards. Demonstrate program value through retention improvements and engagement gains to justify increased investment. Phase program implementation starting with highest-impact elements. Leverage existing resources like internal communication channels rather than requiring new technology investments initially.
Challenge: Remote Team Engagement
Distributed security teams face unique recognition challenges:
Solution: Prioritize digital recognition platforms accessible from anywhere. Record recognition messages for asynchronous viewing across time zones. Integrate recognition into collaboration tools teams already use. Ship physical awards to remote locations. Host virtual recognition ceremonies with interactive elements. Ensure remote workers receive proportional recognition to on-site employees through monitoring and tracking.
Future Trends in Security Team Recognition
AI-Assisted Recognition Programs
Emerging recognition platforms incorporate artificial intelligence capabilities:
Recognition Gap Identification: AI algorithms analyze recognition patterns identifying team members receiving insufficient acknowledgment relative to contributions—surfacing potential oversight.
Personalized Recognition Suggestions: Machine learning recommends recognition approaches most meaningful to individual team members based on preferences and past responses.
Achievement Tracking Automation: AI systems automatically identify certification achievements, training completions, and measurable milestones triggering recognition workflows.
Sentiment Analysis: Natural language processing evaluates team communication detecting recognition opportunities and appreciation gaps.
Blockchain-Based Credential Verification
Distributed ledger technology enables verifiable credential and achievement tracking:
Immutable Achievement Records: Blockchain creates permanent, tamper-proof records of certifications, achievements, and recognitions.
Portable Credential Wallets: Security professionals maintain personal digital wallets containing verified credentials recognized across organizations.
Automated Verification: Instant verification of certifications and achievements eliminating manual validation processes.
Micro-Credentials and Badges: Granular recognition of specific skills and accomplishments through blockchain-backed digital badges.
Integration with Career Development Platforms
Recognition systems increasingly connect with comprehensive career development tools:
Skills Mapping: Recognition tied to competency frameworks showing career progression pathways.
Mentorship Matching: Connect recognized high performers with trainees seeking mentorship in specific security domains.
Succession Planning: Recognition data informs succession planning identifying high-potential security professionals for leadership development.
Learning Recommendations: AI suggests training and development opportunities based on recognition gaps and career goals.
Organizations implementing advanced recognition solutions position themselves to leverage emerging capabilities as they mature while building foundations supporting future enhancement.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity trainee recognition programs address critical workforce challenges facing the security industry: talent shortages, high turnover rates, and burnout among early-career professionals. Organizations investing in comprehensive recognition programs create cultures that value learning, celebrate achievement, and demonstrate clear career progression—ultimately improving retention, boosting morale, and building stronger security teams.
Effective programs combine clear recognition criteria, multiple recognition formats, transparent processes, and connections to career development. They balance individual and team recognition while emphasizing both technical excellence and cultural values. Modern digital recognition displays enable visibility, accessibility, and engagement impossible with traditional approaches—particularly valuable for distributed security teams.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built recognition platforms designed specifically for celebrating professional achievement. These specialized tools offer advantages over generic digital signage including recognition-specific workflows, career progression showcases, certification tracking, and comprehensive analytics measuring program impact.
The cybersecurity talent market will remain intensely competitive for the foreseeable future. Organizations building cultures that genuinely value and recognize security professionals gain significant competitive advantages in attracting, developing, and retaining the skilled teams needed to defend against evolving threats.






















