Key Takeaways
Complete guide to conference championship games across all sports. Learn selection criteria, qualification paths, tiebreakers, championship formats, and how schools preserve these prestigious athletic achievements through modern recognition systems.
The roar of the crowd. Championship banners unfurling. Trophy presentations. For student-athletes across all sports, conference championship games represent pinnacle moments—the culmination of months of preparation, regular season competition, and team dedication converging in single defining contests that determine conference supremacy. Whether watching college football conference championships broadcast nationally the first weekend of December, following high school basketball conference tournaments in February, or tracking volleyball conference championships in November, these championship games showcase athletic excellence while crowning conference champions who earn recognition, NCAA tournament bids, and lasting legacies.
Yet many fans, parents, and even some athletes remain uncertain about how teams actually qualify for conference championship games, what different championship formats exist across sports and conferences, how tiebreakers determine participants when teams finish with identical records, and why these championships matter beyond simple bragging rights. This comprehensive guide explains conference championship game mechanics across sports, explores qualification processes and selection criteria, examines championship formats from single-game showdowns to multi-round tournaments, clarifies playoff implications and automatic bids, and reveals how schools preserve these prestigious achievements through permanent recognition systems ensuring championship teams receive lasting celebration.
Understanding Conference Championships: Structure and Significance
Conference championships exist as organizational structures within competitive athletics where schools group together based on geography, institutional characteristics, or historical relationships to conduct regular season competitions and determine conference champions through structured championship events.
What Defines Athletic Conferences
Athletic conferences represent formal associations of schools agreeing to organize competition within defined membership groups rather than conducting completely independent schedules:
Conference Membership Structures:
Power Conferences: At the highest collegiate levels, “Power Five” conferences (SEC, Big Ten, ACC, Big 12, Pac-12) comprise major research universities with extensive athletic programs, large stadiums, national media coverage, and significant revenue. These conferences typically feature 12-18 members competing across all major sports while conducting high-profile championship events attracting national attention.
Mid-Major Conferences: Schools competing at Division I levels outside Power Five conferences form mid-major conferences like the Mountain West, American Athletic Conference, Conference USA, and numerous others. These conferences often provide automatic NCAA tournament bids to championship winners while allowing strong programs to compete for national recognition.
Small College Conferences: Division II, Division III, NAIA, and junior college conferences organize competition for schools emphasizing different athletic philosophies—balancing athletics with academics, limiting scholarships, or serving regional student populations. These conferences conduct championships with equal competitive intensity despite receiving less national media attention.
High School Conferences: Secondary schools organize into conferences based primarily on geography and school enrollment size, creating competitive balance while minimizing travel burdens for student-athletes. State athletic associations typically oversee conference structures while conducting separate state championship tournaments beyond conference competitions.

Sport-Specific Conference Variations:
Schools don’t necessarily compete in the same conference across all sports. Many institutions maintain different conference affiliations for football versus basketball and Olympic sports due to competitive levels, geographic considerations, or historical relationships. Notre Dame competes as an independent in football while belonging to the ACC for most other sports. Some schools sponsor particular sports in conferences where they don’t hold full membership, creating complex affiliation maps requiring careful tracking.
Why Conference Championships Matter
Conference championships carry significance extending far beyond simple trophy presentations:
NCAA Tournament Implications:
For many sports, winning conference championships earns automatic bids to NCAA tournaments. March Madness selections, volleyball Final Four qualifications, baseball College World Series entries, and numerous other NCAA championship tournaments reserve guaranteed spots for conference tournament champions regardless of regular season records. This automatic qualification transforms conference tournaments into “win-or-go-home” scenarios where teams controlling their own NCAA tournament destiny through championship victories regardless of selection committee evaluations.
National Championship Pathways:
Sports like college football that don’t conduct extensive playoff tournaments still weight conference championships heavily in selection processes. College Football Playoff committee considerations consistently elevate conference champions over non-champions with similar records, making conference championship victories crucial for teams with national championship aspirations. Championship teams earn recognition that propels programs toward higher competitive aspirations.
Recognition and Tradition:
Conference championships become permanent parts of program histories—achievements celebrated decades later through banners, record books, and recognition displays. Schools commemorate conference championships prominently because these titles demonstrate sustained excellence throughout conference seasons, not just single-game victories. Athletic recognition programs preserve championship legacies ensuring current students connect with program traditions.
Recruiting Advantages:
Programs winning conference championships regularly attract stronger recruiting classes. Athletes want to compete for championships, and visible conference championship recognition demonstrates program capability to deliver championship opportunities. Successful programs showcase conference championship history during campus visits, highlighting traditions recruits can join while pursuing their own championship aspirations.
Financial and Exposure Benefits:
Conference championship games generate significant revenue through ticket sales, television rights, and sponsorships. Championship game appearances increase program visibility attracting casual fans, alumni support, and media attention elevating institutional profiles. Successful programs leverage championship visibility into enhanced fundraising, improved facilities, and expanded resources supporting continued competitive excellence.
Conference Championship Formats Across Different Sports
Championship formats vary dramatically across sports based on competition structures, scheduling constraints, and traditional approaches within specific athletic contexts:
Single-Game Championship Models
Some sports conduct conference championships through single winner-take-all contests between top teams:
College Football Conference Championships:
Major college football conferences typically conduct championship games on the first Saturday of December, pitting division winners or top-ranked teams in neutral-site or campus locations for conference supremacy. The SEC Championship between Eastern and Western Division winners, Big Ten Championship between top-ranked East and West teams, and similar formats create high-stakes single games determining conference champions and influencing College Football Playoff selections.
Championship Game Qualification:
Most conferences using championship games divide membership into divisions (typically based on geography) with regular season play determining division winners. Division winners advance automatically to championship games regardless of overall conference records, though some conferences implement ranking systems where top two teams regardless of division compete when division-based formats create mismatches.
Tiebreaker Scenarios:
When multiple teams tie for division leads, conferences apply systematic tiebreaker procedures:
- Head-to-head results between tied teams
- Division records among tied teams
- Records against common conference opponents
- Overall conference winning percentages
- Strength of schedule comparisons
- Rankings in playoff selection systems
- Coin flips or other random selection methods (extremely rare)
These tiebreakers can create controversial outcomes where teams with identical conference records receive different championship opportunities based on head-to-head results or strength of schedule differentials.

High School Football Conference Championships:
Many high school conferences crown football champions based on regular season records without conducting separate championship games due to state playoff format considerations. Some conferences conduct championship games on final regular season weekends, though state playoff structures often supersede conference championship importance.
Multi-Round Tournament Models
Many sports conduct bracket-style conference tournaments determining champions through elimination or pool-play formats:
Basketball Conference Tournaments:
College basketball conferences conduct post-season tournaments separate from NCAA tournaments, typically in late February through mid-March. Tournament formats vary:
Single-Elimination Brackets: Most conferences use single-elimination formats where losing teams are immediately eliminated. Tournament seeding typically reflects regular season standings, with top seeds receiving first-round byes and favorable bracket positions.
Conference Tournament Size: Some conferences include all member schools (Big Ten’s 14-team tournament), others limit participation to top finishers (SEC traditionally used top-12 format before recent expansion).
Neutral Sites vs. Campus Locations: Many conferences conduct tournaments at neutral-site arenas providing travel equity and hosting city economic benefits. Others award higher seeds home-court advantage for early rounds, moving to neutral sites for championships.
Tournament Duration: Most basketball tournaments span 3-4 days with multiple games daily, creating compressed competition requiring depth and conditioning. Youth sports award programs recognize tournament performance excellence alongside regular season achievements.
Basketball Championship Qualification:
In basketball, regular season records determine tournament seeding and first-round bye distribution. Conference tournament champions receive automatic NCAA tournament bids, making these tournaments critically important for bubble teams needing championship victories to secure March Madness invitations. Even top-seeded teams prioritize conference tournament success due to NCAA tournament seeding implications and championship tradition significance.
Baseball and Softball Tournaments:
Spring sports typically conduct multi-day tournaments featuring pool play followed by elimination brackets. Baseball and softball conference tournaments commonly span 4-5 days with multiple games daily, testing pitching depth and roster capabilities while determining automatic NCAA tournament qualifiers.
Tournament formats typically include:
- Pool play dividing teams into groups competing round-robin
- Elimination brackets for top pool finishers
- Double-elimination formats giving teams second chances after initial losses
- Championship finals determining conference champions and NCAA automatic qualifiers
Volleyball and Other Fall Sports:
Volleyball conferences conduct post-season tournaments typically using four-team or eight-team single-elimination brackets with higher seeds hosting early rounds. Championship matches often move to neutral sites or regular season champion home venues, determining NCAA automatic qualifiers while providing redemption opportunities for teams that didn’t win regular season titles.

Regular Season Championship Determination
Some conferences crown champions based solely on regular season records without separate championship games or tournaments:
Regular Season Title Sports:
Many Olympic sports—swimming, track and field, cross country, soccer, lacrosse—determine conference champions through regular season competition culminating in conference championship meets or tournaments that crown champions but don’t function as elimination events. All competitors participate in championship meets earning points based on placement, with highest team point totals claiming conference championships.
Dual Meet vs. Championship Meet Formats:
Sports like wrestling, swimming, and gymnastics conduct regular seasons through dual meets (head-to-head team competitions) while hosting season-ending championship meets where all conference schools compete simultaneously. Teams earn points based on individual athlete placements, with cumulative scores determining conference champions.
These championship meet formats test program depth because success requires multiple contributors placing highly across numerous events rather than relying on few star performers. Teams winning regular season dual meet titles sometimes lose championship meets to programs with greater depth achieving more cumulative points through widespread solid performances.
Tiebreaker Considerations:
When teams finish regular seasons with identical conference records, systematic tiebreakers determine champions:
- Head-to-head results (if teams met during regular season)
- Records against next-highest-ranked conference teams
- Overall winning percentages including non-conference games
- Strength of schedule metrics
- Points differential in conference games
- Ranking in national polls or rating systems
- Random selection methods if all other tiebreakers fail
Some conferences designate co-champions when teams tie and tiebreakers don’t clearly distinguish superiority, celebrating multiple programs rather than forcing artificial distinctions.
Qualification Paths: How Teams Earn Championship Opportunities
Understanding precisely how teams qualify for conference championships requires examining sport-specific selection criteria and advancement mechanisms:
Division-Based Qualification Systems
Sports using divisional structures typically advance division winners automatically:
Football Division Structures:
Most major college football conferences divide membership into two divisions creating balanced competition within geographic groupings. The SEC’s Eastern Division (Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, South Carolina, Tennessee, Vanderbilt, Missouri) and Western Division (Alabama, Arkansas, Auburn, LSU, Mississippi State, Ole Miss, Texas A&M) compete for division titles with winners advancing to the SEC Championship Game in early December.
Division Standing Determination:
Division standings rely on conference game results specifically against division opponents. Teams earning best division records claim division titles and championship game berths. When multiple teams tie for division leads, head-to-head results typically break ties, followed by division record against common opponents, overall conference records, and other systematic criteria.
Cross-Divisional Play Impact:
Conference schedules include both division games and cross-divisional matchups. While cross-divisional results count toward overall conference standings and tiebreaker considerations, division records primarily determine division champions. This structure can create scenarios where teams with worse overall conference records win divisions due to favorable division-specific results.

Championship Game Participation Rules:
Most conferences require teams to achieve minimum eligibility standards (typically .500 overall records) to participate in championship games even when winning divisions. This prevents teams with losing overall records despite division titles from championship game appearances, though exceptions occasionally occur when no division teams meet thresholds.
Seeding-Based Tournament Qualification
Sports conducting conference tournaments typically seed participants based on regular season conference standings:
Tournament Seeding Methodologies:
Regular season conference records determine tournament seeds with highest winning percentages earning top seeds and accompanying advantages:
Top-Seed Benefits:
- First-round byes skipping opening games
- Home-court or home-field advantage in early rounds
- Favorable bracket placement avoiding toughest opponents until later rounds
- Additional rest and preparation time compared to lower seeds
Seeding Tiebreakers:
When teams finish with identical conference records, tiebreakers establish tournament seeding:
- Head-to-head results (team winning season series receives higher seed)
- Record against highest-ranked common opponent
- Record against next-highest-ranked opponents working down standings
- Scoring differential in head-to-head games
- Overall win-loss records including non-conference games
- NCAA NET rankings or other selection metric systems
- Random selection if all distinguishing criteria tied
These tiebreakers can significantly impact tournament outcomes—difference between 3-seed and 4-seed often determines championship game path difficulty and potential opponent matchups in bracket structures.
Automatic Qualification vs. Limited Fields:
Some conference tournaments include all member schools (Big Ten basketball’s 18 teams), while others limit participation to top regular season finishers. The athletic competition intensity throughout regular seasons increases when teams compete for tournament qualification rather than just seeding position.
At-Large and Wild Card Considerations
Some championship formats include wild card positions or at-large qualifications beyond division winners:
Football Wild Card Concepts:
While most college football conference championships pit division winners head-to-head, some conferences explored alternatives during recent realignment. The Big 12, lacking divisions after earlier membership changes, sends the top two teams based on overall conference records to its championship game, essentially making both teams “at-large” qualifiers rather than predetermined division representatives.
Basketball Tournament At-Large Concepts:
College basketball conference tournaments typically include multiple teams beyond just division leaders—often top 10-14 teams from conference standings receive tournament invitations. Lower-seeded teams must win multiple games to capture championships, creating “Cinderella” scenarios when underdogs string together tournament victories claiming automatic NCAA tournament bids despite mediocre regular seasons.
Play-In Game Structures:
Some conference tournaments use play-in games where bottom-seeded teams compete for final bracket positions. These games provide additional championship participation opportunities while creating elimination pressure on tournament’s first day, generating excitement throughout tournament duration.
Championship Week Scheduling and Logistics
Conference championships involve complex logistical coordination balancing competitive fairness with practical scheduling constraints:
Neutral Site Championships
Many conferences conduct championship events at predetermined neutral-site locations providing competitive balance while maximizing fan access and revenue potential:
Football Neutral Site Benefits:
Major conference football championships typically occur in large metropolitan stadiums:
- Mercedes-Benz Stadium (Atlanta) hosts SEC Championship
- AT&T Stadium (Dallas) hosts Big 12 Championship
- Allegiant Stadium (Las Vegas) hosts Pac-12 Championship
- Lucas Oil Stadium (Indianapolis) hosts Big Ten Championship
Neutral sites prevent home-field advantages, accommodate larger crowds than most campus stadiums, and create destination events attracting national media attention. Host cities benefit economically from championship visitor spending, creating municipal support for long-term hosting agreements.
Basketball Tournament Cities:
College basketball conferences traditionally conduct tournaments in major cities with large arenas and entertainment districts:
- Madison Square Garden (New York) hosts Big East Tournament
- United Center (Chicago) hosts Big Ten Tournament
- Sprint Center (Kansas City) hosts Big 12 Tournament
- Barclays Center (Brooklyn) hosts ACC Tournament
These locations create exciting atmospheres while providing neutral settings, though geographic centrality varies—West Coast teams traveling to East Coast tournaments face greater burdens than regional schools.

Campus Site Championships:
Some conferences award championship game hosting rights to higher-seeded teams or regular season champions, creating home-field advantages but recognizing regular season excellence:
Competitive Implications: Home teams typically perform better due to familiar surroundings, supportive crowds, eliminated travel fatigue, and psychological advantages competing in comfortable environments.
Financial Considerations: Campus championships allow institutions to retain ticket revenue and concession sales rather than sharing with neutral-site venues, benefiting athletic department budgets while rewarding successful regular seasons.
Logistical Challenges: Campus hosting requires adequate facility capacities, proper infrastructure, and ability to accommodate visiting teams and media contingents. Smaller venues might lack sufficient seating for championship demand or necessary broadcast facilities for television production.
Scheduling Considerations and Rest Periods
Championship scheduling balances competitive fairness with practical calendar constraints:
Rest Day Allocations:
Tournament formats typically provide minimal rest between games—often less than 24 hours in basketball conference tournaments. This compressed scheduling tests roster depth, conditioning, and injury management while creating exciting consecutive-day atmospheres for fans.
Higher tournament seeds sometimes receive bye-day advantages, resting while lower seeds compete in first-round games. This rewards regular season excellence while creating competitive differentiation between top programs and lower-seeded challengers.
Travel Logistics:
Neutral-site championships require coordinated travel arrangements ensuring all potential championship participants can reach venues regardless of late-notice confirmations. Schools prepare contingency travel plans since semifinal losers won’t need championship game transportation while winners require immediate booking adjustments.
Academic Considerations:
Conference championships occurring during academic calendar periods require balancing athletic participation with educational responsibilities. Student-athletes miss classes for travel and competition, necessitating academic support coordination, make-up work arrangements, and communication with faculty ensuring educational progress continues during championship weeks. Many institutions implement student recognition programs celebrating athletes maintaining academic excellence alongside athletic achievement.
Tiebreaker Scenarios and Controversial Determinations
Conference championship qualification sometimes hinges on complex tiebreaker applications determining which teams advance when multiple programs finish with identical records:
Common Tiebreaker Hierarchies
Most conferences publish detailed tiebreaker procedures establishing clear precedence orders:
Primary Tiebreaker - Head-to-Head Results:
When two teams tie, their head-to-head result typically determines the higher standing. The team winning the regular season matchup receives the tiebreaker advantage and higher seed or championship game invitation.
Three-or-More-Team Tie Complications:
Head-to-head tiebreakers become complicated when three or more teams tie. If one team defeated all other tied teams, it wins the tiebreaker. If circular results exist (Team A beat Team B, Team B beat Team C, Team C beat Team A), conferences proceed to subsequent tiebreaker criteria.
Secondary Tiebreaker - Division Records:
For sports using divisions, tied teams’ records specifically against divisional opponents often serve as secondary tiebreakers. Teams with better division records receive advantages over those with worse division records despite identical overall conference records.
Tertiary Tiebreaker - Common Opponent Records:
Conferences compare tied teams’ records against common opponents—teams both schools played during regular seasons. The team with better records against shared opponents wins this tiebreaker, theoretically demonstrating superior performance against equivalent competition.
Strength of Schedule Comparisons:
Advanced tiebreakers sometimes incorporate strength of schedule metrics evaluating opponent quality. Teams that played more difficult conference schedules may receive tiebreaker advantages over those facing easier paths despite identical win-loss records.

Random Selection Methods:
When all systematic tiebreakers fail to distinguish tied teams, conferences employ random selection—coin flips, drawing lots, or other arbitrary methods. While seemingly unfair, random selection provides final resolution preventing indefinite tiebreaker cycles.
Historical Controversial Tiebreaker Decisions
Conference championship history includes numerous controversial tiebreaker applications generating debate about fairness and appropriate criteria:
Division Record Controversies:
Scenarios where teams with worse overall conference records win divisions due to favorable division-specific results create controversy. Critics argue overall conference achievement should outweigh arbitrary divisional alignment, while defenders maintain division structures intentionally separate groupings warranting independent determination.
Three-Team Tie Complications:
Complex three-team ties occasionally produce counterintuitive results where the team with the worst record against the other two tied teams advances due to subsequent tiebreaker advantages. These situations arise from multi-layered tiebreaker applications that, while systematic and predetermined, can generate results seeming illogical when examined in isolation.
Late-Season Rule Changes:
Conferences occasionally modify tiebreaker procedures mid-season or between seasons, creating perception of rules manipulation favoring specific outcomes. While intended to clarify ambiguities or address unforeseen circumstances, timing raises concerns about fairness and transparency.
Tiebreaker Prevention Strategies
Programs hoping to avoid tiebreaker uncertainty implement strategies controlling championship destiny through clear victories:
Dominant Conference Records:
Teams winning conference games by sufficient margins to avoid ties completely eliminate tiebreaker concerns. Going undefeated or losing just one conference game typically secures championship positions without requiring tiebreaker applications.
Head-to-Head Priority:
Understanding head-to-head results serve as primary tiebreakers, teams emphasize key conference matchups against division rivals or top-ranked opponents. Winning these games provides tiebreaker insurance if subsequent losses create standing ties.
Division Game Emphasis:
In division-based structures, teams prioritize division games knowing these results carry greater championship qualification weight than cross-division contests. Programs optimize preparation and resources toward division games when tiebreakers might determine championships.
Championship Game Recognition and Legacy Preservation
Conference championships create lasting program legacies requiring systematic recognition ensuring these achievements receive appropriate celebration:
Traditional Recognition Methods
Schools commemorate conference championships through various physical recognition approaches:
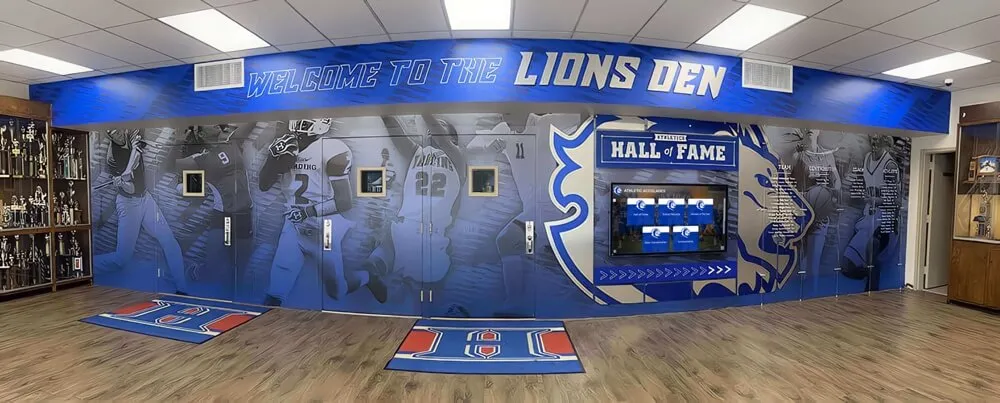
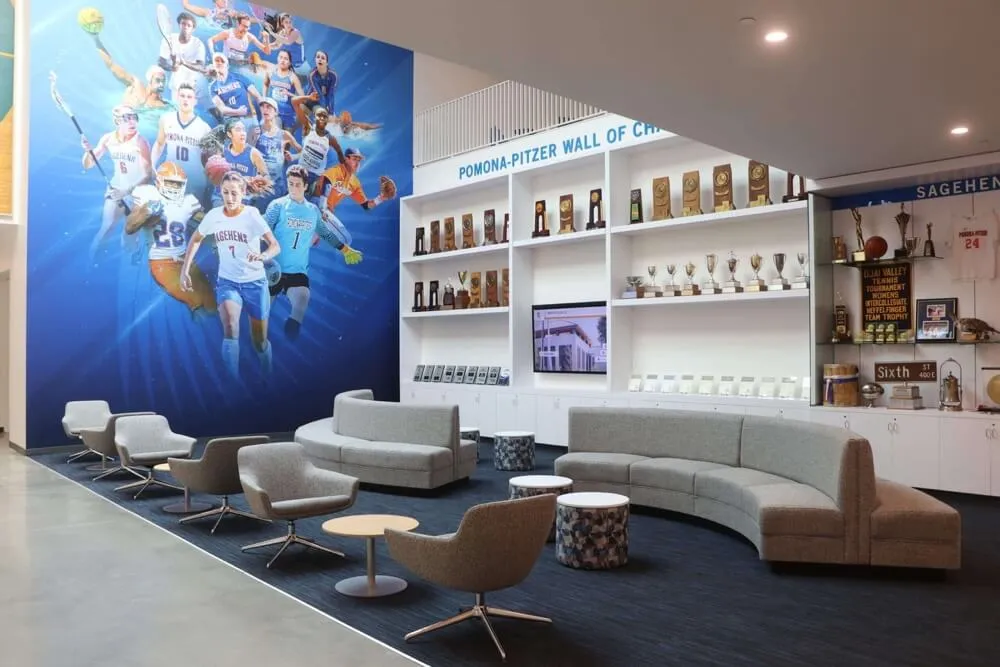
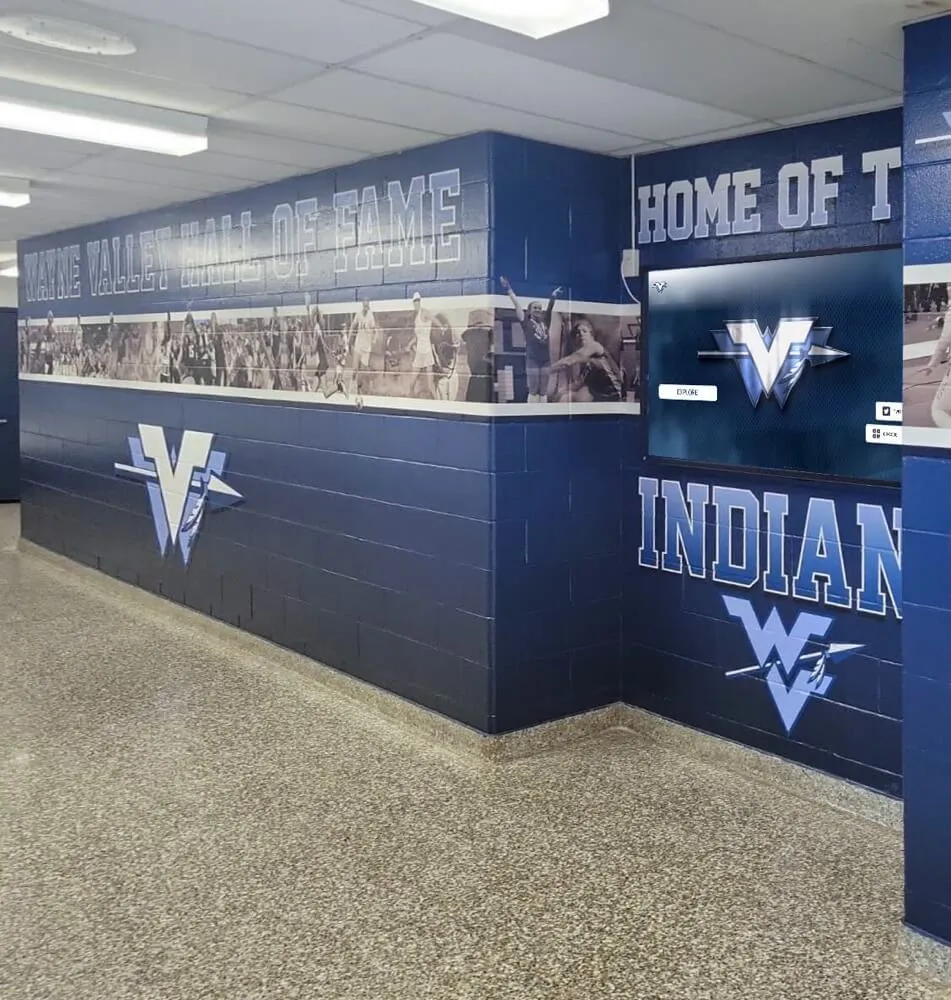
Championship Banners:
Athletic facilities typically display championship banners celebrating conference titles. These fabric banners hung from gymnasium rafters or mounted on arena walls provide visible recognition of program excellence, creating impressive displays demonstrating tradition and success to recruits, fans, and visitors.
Banner formats vary by institution and sport—some schools hang separate banners for each championship, others create composite banners listing multiple championship years for specific sports, and certain programs design elaborate banner displays incorporating conference logos, championship dates, and commemorative imagery.
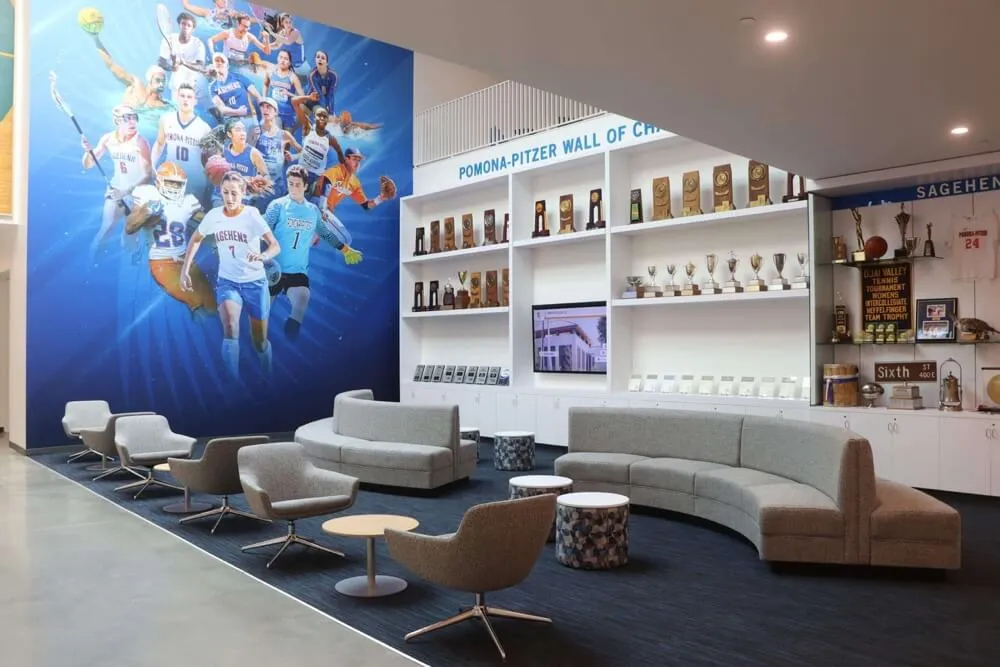
Trophy Cases:
Physical trophies won through conference championship victories typically reside in dedicated trophy cases in athletic facilities, administration buildings, or student commons areas. These displays showcase tangible championship artifacts while providing focal points for school pride and program tradition. Trophy display systems create impressive visual impacts celebrating championship achievements.
Record Boards:
Athletic facilities feature record boards documenting championship achievements alongside individual performance records. These boards preserve championship history while providing context for program excellence across different sports and eras, demonstrating sustained competitive success.
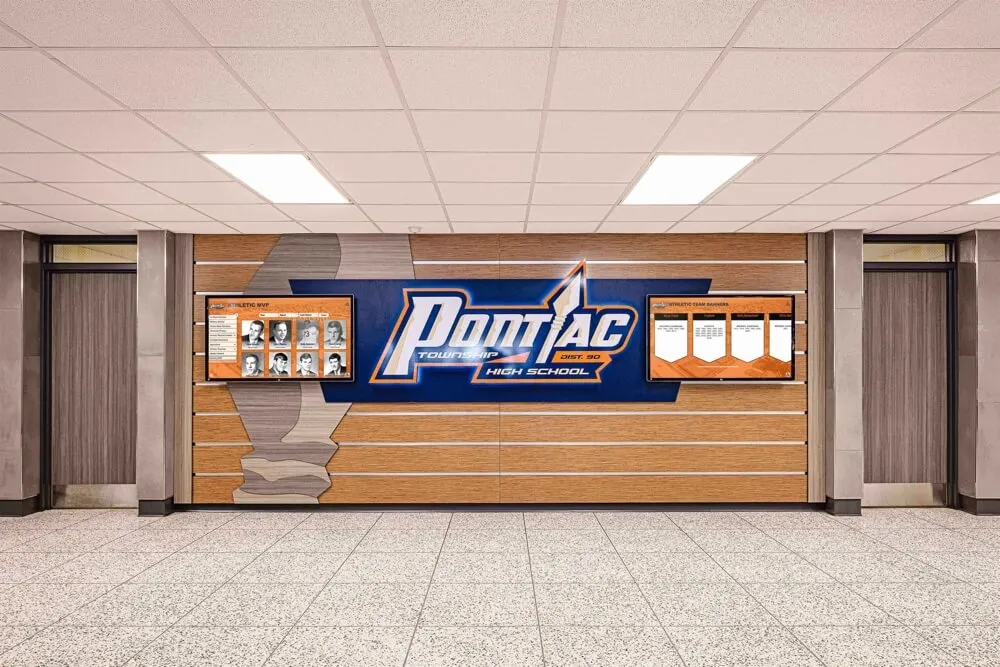
Commemorative Signage:
Schools install permanent signage recognizing championship achievements—plaques, nameplates, or decorative elements incorporated into facility architecture celebrating specific championship teams, seasons, or individuals.

Modern Digital Recognition Advantages
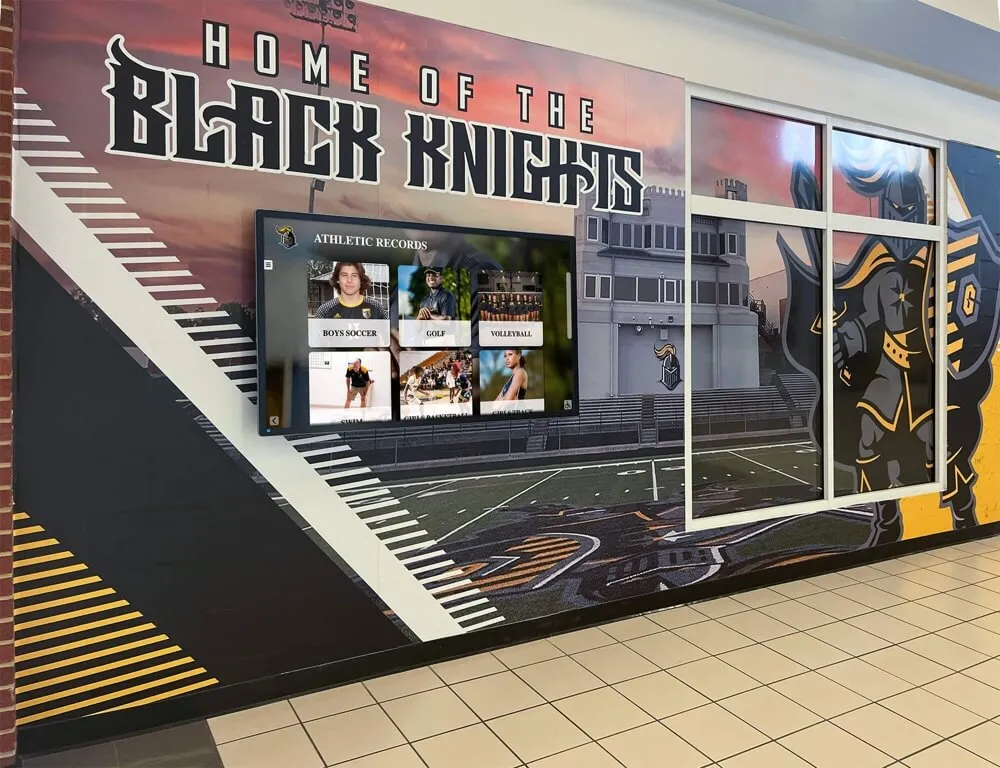
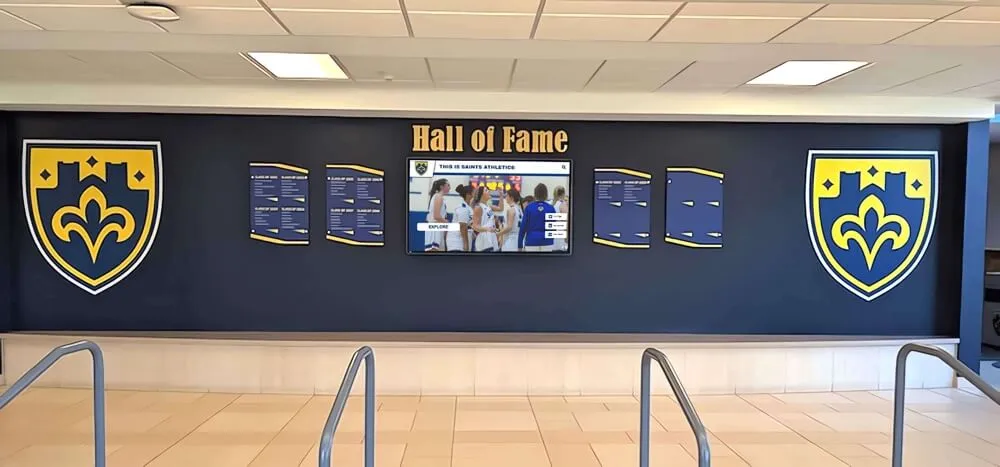
Contemporary schools increasingly leverage digital recognition technology overcoming traditional method limitations:
Unlimited Recognition Capacity:
Physical championship recognition faces space constraints—facilities eventually run out of wall space for banners, display case room for trophies, or architectural locations for plaques. Digital recognition platforms accommodate unlimited championship celebrations without physical space limitations.
Schools can honor every conference championship across all sports throughout program histories—from inaugural championships decades ago through current season victories—without selecting which achievements receive visible recognition versus storage in forgotten archives.
Comprehensive Championship Documentation:
Digital platforms enable rich championship celebration including:
Championship Team Rosters: Complete team lists with every athlete and coach contributing to championship success Season Summaries: Narratives documenting championship season journeys from preseason through championship victories Game Recaps: Detailed championship game descriptions celebrating key plays, standout performances, and defining moments Photo Galleries: Visual documentation of championship celebrations, game action, trophy presentations, and team celebrations Video Highlights: Championship game highlights, season montages, and interview clips preserving memories Statistical Documentation: Complete championship season statistics, performance metrics, and record comparisons
This comprehensive documentation transforms championship recognition from simple banner dates into engaging storytelling preserving complete championship narratives.
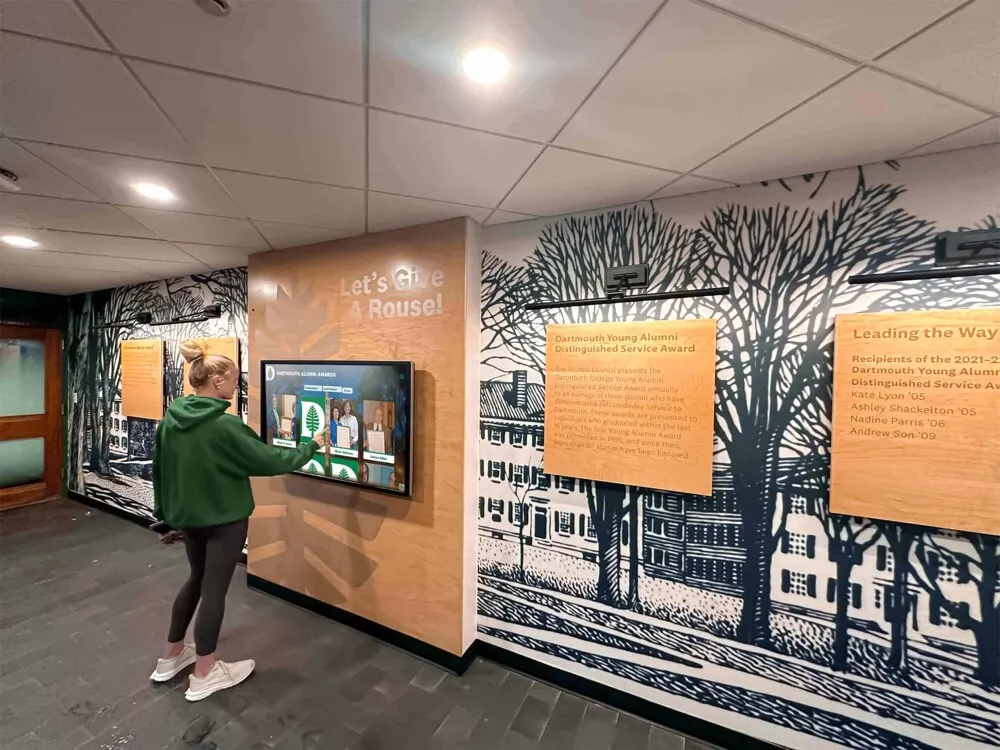
Interactive Exploration Features:
Modern digital displays enable audiences to actively explore championship histories:
Search Functionality: Find specific championship teams, seasons, sports, or individuals instantly Filtering Options: Browse championships by sport, decade, championship type, or other criteria Comparison Tools: Compare championship teams across eras analyzing statistical achievements Social Sharing: Share championship content on social media extending recognition visibility Mobile Access: View championship recognition from smartphones and tablets beyond physical displays
Interactive features engage audiences in championship history exploration creating memorable experiences impossible with static traditional recognition.
Real-Time Updates:
Cloud-based digital systems enable instant recognition updates. When teams win conference championships, athletic departments can update recognition displays immediately—sometimes before championship trophies return to campus.
This immediacy maintains recognition relevance and timeliness. Recent championships receive prompt celebration while historical championships remain permanently accessible, creating dynamic recognition systems honoring both current achievement and longstanding tradition.
Cost-Effective Scalability:
While digital recognition requires higher initial investment compared to single championship banners, long-term economics favor digital approaches. Physical recognition incurs ongoing costs with each new championship—additional banners, trophy cases, plaques, or signage multiplying expenses over decades.
Digital platforms accommodate unlimited championship additions without incremental costs beyond modest annual software subscriptions. Schools achieve cost neutrality within several years while gaining dramatically superior recognition capabilities.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built platforms specifically designed for athletic championship recognition rather than generic digital signage requiring extensive customization. These specialized systems deliver intuitive content management, professional templates, and ongoing support ensuring schools maintain impressive championship recognition without requiring technical expertise.
Integrating Championships Within Broader Recognition
The most effective recognition systems integrate conference championships within comprehensive athletic honor programs celebrating diverse achievements:
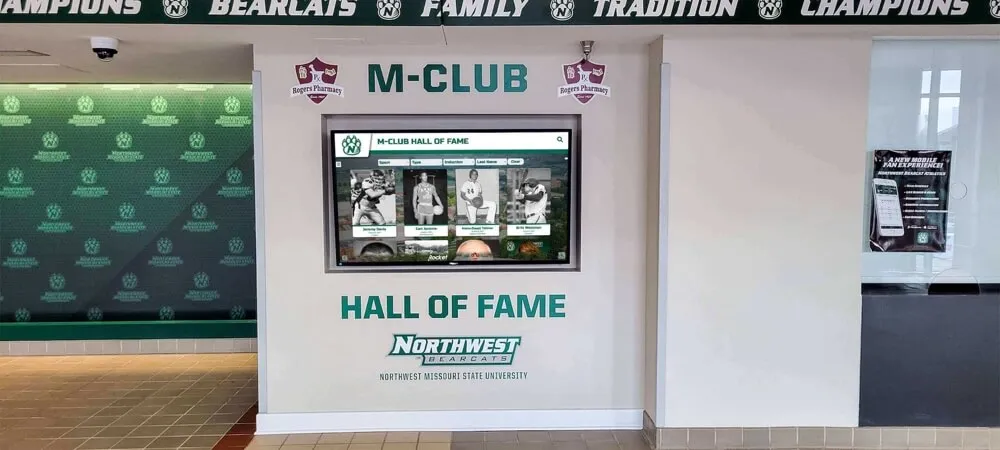
Hall of Fame Integration:
Conference championship team members often receive hall of fame consideration as achievements warranting permanent recognition. Digital platforms can link individual athlete profiles to championship team pages, connecting personal achievements with collective success. Understanding athletic hall of fame structures helps schools develop integrated recognition systems.
Record Board Connections:
Championship seasons often produce record-setting performances. Recognition systems connecting championship teams to individual records set during championship campaigns provide context demonstrating how individual excellence and team success intersect.
All-Conference and Individual Award Recognition:
Championship teams typically feature multiple all-conference selections and individual award winners. Comprehensive recognition celebrates these individual honors alongside team championships, acknowledging both collective achievement and personal excellence contributing to championship success.
Coach Milestone Recognition:
Conference championships mark coaching career milestones worth celebrating. Digital platforms can highlight coaches’ championship accomplishments, career records, and program building achievements alongside team recognitions, honoring mentors who developed championship programs.

Conference Championship Impact on NCAA Selection
Conference championship outcomes significantly influence NCAA tournament selections, seeding, and championship opportunities:
Automatic Qualifier Implications
Most NCAA tournaments award automatic bids to conference tournament or regular season champions:
Basketball Automatic Bids:
All 32 Division I basketball conferences receive automatic NCAA tournament bids for their conference tournament champions. This structure means winning conference tournaments guarantees March Madness participation regardless of regular season record or selection committee opinions.
This automatic qualification transforms conference tournaments into “win-and-in” scenarios where teams controlling NCAA tournament destiny through championship victories. Bubble teams facing uncertain at-large selection possibilities eliminate doubt by winning conference tournaments, while top-seeded favorites risk NCAA tournament exclusion if losing early to lower seeds.
Olympic Sports Automatic Qualifiers:
Most NCAA championship tournaments across Olympic sports—volleyball, soccer, baseball, softball, lacrosse, etc.—award automatic bids to conference champions. Championship selection methods vary (some reward regular season champions, others conduct conference tournaments), but the principle remains consistent: conference champions earn NCAA championship tournament invitations.
Football Playoff Considerations:
College football’s limited playoff structure (four teams expanding to 12 in recent years) doesn’t provide automatic bids for all conference champions, but championship victories significantly influence selection committee deliberations. Conference champions typically receive preferential consideration over non-champions with similar records, making conference championship victories important for playoff aspirations.
Seeding Advantages
Beyond automatic qualification, conference championship success influences NCAA tournament seeding:
Basketball Seeding Impact:
NCAA tournament selection committee heavily weights conference tournament performance when establishing tournament seeds. Teams winning conference tournaments demonstrate current form and competitive excellence earning higher NCAA seeds and favorable bracket positions.
Conversely, early conference tournament losses can damage NCAA seeding—teams entering conference tournaments as projected 3-seeds might fall to 5-seeds or 6-seeds after disappointing tournament showings, significantly impacting NCAA championship paths.
Momentum Considerations:
Selection committees acknowledge that teams entering NCAA tournaments on winning streaks after conference championship victories often carry momentum advantages. While difficult to quantify, recent championship success can influence close seeding decisions between comparable teams.
At-Large Selection Implications
Conference championship results affect at-large NCAA tournament selection for teams not winning championships:
Bubble Team Dynamics:
Teams on NCAA tournament selection bubble benefit from strong conference tournament performances even without winning championships. Reaching conference championship games or semifinals demonstrates competitive level worthy of NCAA inclusion, helping bubble teams secure at-large bids.
Conversely, early conference tournament exits by bubble teams often result in NCAA tournament exclusion. Selection committees interpret first-round losses as evidence teams lack championship capability, directing at-large bids elsewhere.
Resume Building:
Deep conference tournament runs build selection resumes through quality wins against tournament-tested opponents. These victories provide recent evidence of team capabilities carrying greater weight than games played weeks earlier during regular seasons.

Creating Championship Culture Through Recognition
Schools building sustained championship programs leverage recognition systems creating cultures where championship pursuit becomes institutional identity:
Visible Achievement Standards
Comprehensive championship recognition establishes visible excellence standards inspiring current athletes:
Aspirational Benchmarks:
When athletes enter facilities immediately seeing decades of conference championship recognition, they understand program expectations and achievement standards. Championship tradition visibility answers the question “What’s possible here?” demonstrating that championship success represents realistic possibilities, not distant fantasies.
Digital displays showcasing championship teams from multiple eras communicate that championship achievement occurs regularly within programs, not as rare exceptions. This normalization of championship success builds confidence that current athletes can similarly achieve excellence through preparation and commitment.
Specific Path Models:
Championship recognition featuring detailed season narratives provides models illustrating how teams reached championship success. Current athletes learn from championship team journeys—early season adversity, mid-season adjustments, late-season momentum—understanding that championship paths vary but dedication and improvement enable championship opportunities.
Alumni Connection and Mentorship
Championship recognition creates bridges connecting current athletes with program alumni:
Mentorship Opportunities:
Schools can facilitate connections between current athletes and championship team alumni, creating mentorship relationships where former champions share experiences, provide guidance, and inspire current competitors. Alumni engagement programs strengthen these connections supporting current athlete development.
Reunion Events:
Championship team reunions marking significant anniversaries (10-year, 25-year, 50-year) bring former champions to campus interacting with current programs. These events create memorable experiences for current athletes meeting program legends while strengthening alumni connections supporting program resources and advocacy.
Continuity and Tradition:
Visible championship recognition spanning decades demonstrates program continuity and sustained excellence. Current athletes understand they’re contributing to ongoing traditions rather than isolated seasons, creating deeper meaning in daily preparation and competition.
Recruiting Advantages
Championship recognition provides powerful recruiting tools demonstrating program competitive capabilities:
Campus Visit Impact:
When recruits visit campuses, championship recognition displays showcase program excellence immediately. Comprehensive digital displays featuring multiple championship teams across different eras demonstrate consistent success, not fluky single-season achievements.
Recruits envision themselves potentially joining future championship teams, understanding that programs regularly competing for and winning conference championships provide legitimate paths toward championship experiences and competitive excellence.
Digital Recruiting Materials:
Web-based championship recognition enables remote recruiting demonstrations. Programs can share championship recognition links with recruits nationwide, showcasing program traditions and championship culture without requiring in-person campus visits.
Social media integration allows programs to regularly celebrate championship anniversaries, share championship content, and maintain championship visibility throughout recruiting cycles, reinforcing messages about program competitive capabilities.
Institutional Pride and Community Support
Championship recognition extends beyond athletic departments, building broader institutional pride and community engagement:
Student Body Engagement:
Visible championship recognition increases non-athlete student awareness and pride in institutional athletic achievements. When students regularly encounter championship displays walking through campus, they develop stronger connections to athletic programs and greater likelihood of attending events supporting teams.
Alumni Giving:
Championship recognition reminds alumni of positive institutional experiences, encouraging continued engagement and philanthropic support. Alumni who competed on championship teams or attended schools during championship eras maintain strong emotional connections strengthened through continued championship recognition visibility.
Community Identity:
For schools where athletics significantly contribute to community identity—particularly in smaller communities where high school athletics provide primary entertainment and pride sources—championship recognition reinforces positive community connections. Athletic recognition programs create engaging experiences celebrating community athletic heritage.
Conclusion: Celebrating Championship Excellence
Conference championship games represent pinnacle competitive moments across all athletic levels—from Power Five college football championships broadcast to millions through high school conference basketball tournaments determining local supremacy. These championships matter deeply because they recognize sustained excellence throughout regular season competition, provide pathways to national championship opportunities through automatic NCAA tournament bids, and create lasting legacies celebrated by programs, athletes, alumni, and communities for generations.
Understanding how teams qualify for conference championships—whether through division-based systems automatically advancing division winners, seeding-based tournament structures rewarding regular season excellence, or regular season championship determinations based on cumulative competition—clarifies the competitive processes determining which teams earn championship opportunities. Complex tiebreaker hierarchies ensure fair determinations when teams finish with identical records, though occasionally controversial applications generate debate about appropriate criteria and fairness.
Championship formats vary dramatically across sports and conferences, from single-game winner-take-all football championships to multi-day basketball tournaments to championship meets determining Olympic sport supremacy through cumulative point totals. Each format creates unique competitive dynamics, scheduling challenges, and excitement for participants and fans while serving the fundamental purpose of determining conference champions worthy of recognition and celebration.
Beyond immediate competitive implications, conference championships carry lasting significance through NCAA tournament automatic qualifications, seeding advantages, and at-large selection influences. Championship victories open doors to national championship pursuits while building program reputations attracting talented recruits, enhanced resources, and sustained competitive excellence.
Modern recognition technology transforms how schools celebrate conference championships, moving beyond space-constrained physical banners and trophy cases toward comprehensive digital platforms accommodating unlimited championship recognition with rich multimedia documentation, interactive exploration features, and real-time updates. These systems preserve championship legacies while maintaining dynamic connections between historical achievements and current program activities, creating cultures where championship pursuit becomes institutional identity inspiring sustained excellence.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built platforms specifically designed for athletic championship recognition, delivering intuitive content management, professional design templates, and comprehensive support enabling schools to celebrate conference championships appropriately without requiring technical expertise. Whether recognizing historic championship teams from decades past or celebrating current season victories, digital recognition ensures these prestigious achievements receive lasting visibility and celebration they deserve.
Conference championships represent more than single-game victories or tournament trophies—they embody months of preparation, collective dedication, sustained excellence throughout competitive seasons, and defining moments when teams achieve their full potential. Effective recognition systems honor these achievements while inspiring future generations to pursue their own championship opportunities, creating self-reinforcing cycles of excellence that distinguish championship programs from ordinary competitors.
Explore comprehensive championship recognition solutions that celebrate athletic excellence through modern digital technology, preserving conference championship legacies while building championship cultures inspiring sustained competitive success across all sports and competitive levels.